Gas Fees Trends in Ethereum are a critical aspect of network transaction costs. As of September 2024, trends indicate notable fluctuations, influenced by factors such as Layer-2 solutions and recent upgrades like EIP-4844. Gas fees have remained relatively low, providing a more cost-effective environment for both developers and users. This article delves into the latest trends, examining how these changes impact network usage, transaction costs, and developer activity.
Overview of Gas Fees Trends in Ethereum September 2024
As of September 2024, Ethereum gas fees have continued their downward trend, presenting a more affordable landscape for users and developers. This decline is attributed to key upgrades like Layer-2 scaling solutions and EIP-4844, which have optimized network efficiency. This section delves into the day-to-day fluctuations of gas fees and the major factors driving these reductions, offering insights into how they are impacting Ethereum’s ecosystem.
Real-Time Gas Fee Trends
Ethereum’s gas fees have shown daily fluctuations throughout September 2024, reflecting varying levels of network congestion and usage. The average gas fee for most transactions, including swaps and NFT sales, has hovered around 27.53 Gwei. This is a significant reduction from earlier months, which saw gas fees as high as 40+ Gwei during periods of heightened network activity. In particular, high-consumption protocols like Uniswap and Maestro Router continue to influence spikes in fees during peak periods.
For NFT transactions and smart contract deployments, gas fees have experienced more volatility, often reflecting the network’s congestion. For instance, simple transfers cost less than complex smart contract interactions, and the fee for processing NFT sales can surge significantly during popular drops. Monitoring real-time Ethereum gas fees has become vital for developers and users seeking cost-effective transaction timing.
Factors Driving Gas Fee Reductions
The reduction in Ethereum gas fees can be largely attributed to the implementation of Layer-2 solutions such as Optimism and Arbitrum, which offload much of the transaction volume from Ethereum’s main chain. These solutions have allowed for faster, cheaper transactions, particularly for decentralized finance (DeFi) and decentralized applications (dApps), reducing congestion on Ethereum’s base layer.
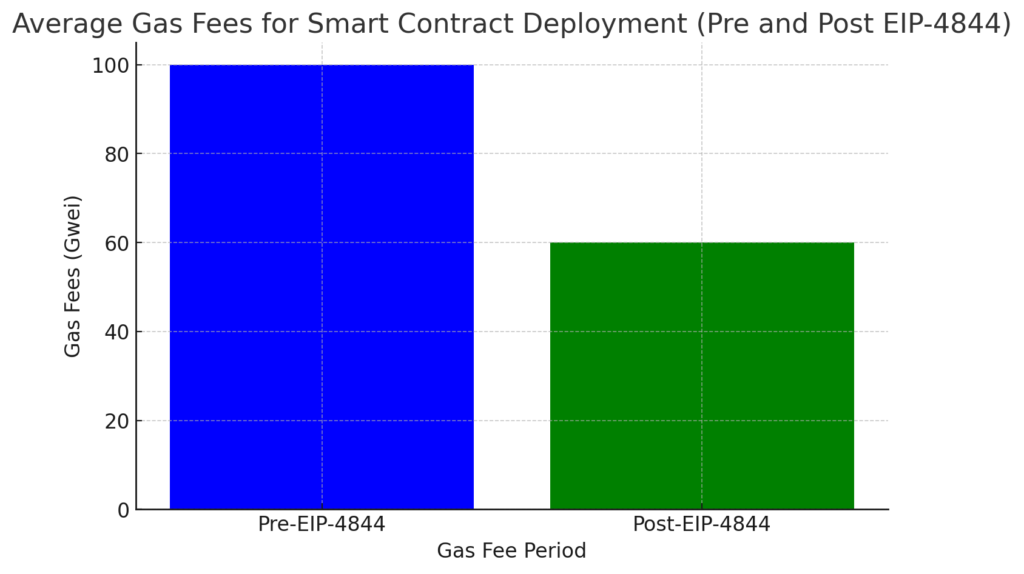
Another key factor is the deployment of EIP-4844, which introduced Proto-Danksharding, a significant network upgrade aimed at enhancing data availability on Ethereum. This upgrade has further streamlined how the network handles large-scale data transactions, effectively lowering the gas fees associated with them. The table below compares the average gas fees before and after these upgrades for different transaction types:
| Transaction Type | Average Fee Pre-EIP-4844 (Gwei) | Average Fee Post-EIP-4844 (Gwei) |
|---|---|---|
| Swap (Uniswap) | 50 Gwei | 28 Gwei |
| Smart Contract Deployment | 100 Gwei | 60 Gwei |
| Simple Transfer | 30 Gwei | 15 Gwei |
Impacts on Network Usage and Developer Activity
The substantial decrease in gas fees has spurred renewed interest in Ethereum from both users and developers. Many developers who had previously migrated to other blockchains due to high fees are now returning, attracted by the more affordable environment. As a result, the number of dApp deployments and smart contract interactions has risen steadily throughout September 2024.
For users, lower gas fees mean they can participate more actively in DeFi protocols, execute transactions on NFT platforms, and engage in everyday activities without worrying about prohibitive costs. This has also led to an increase in Ethereum network adoption, with more developers choosing to build their projects on Ethereum rather than competing blockchains, further boosting its ecosystem.
Related articles
Effects of Gas Fee Changes on Smart Contract Costs
The dramatic reduction in Ethereum gas fees has reshaped how developers approach deploying and interacting with smart contracts. As of September 2024, Ethereum is experiencing historically low gas fees, creating new opportunities for decentralized application (dApp) development. With the financial barrier of high transaction costs lowered, both new and established developers are reinvigorated, contributing to Ethereum’s long-term growth.
Cost Reduction for Smart Contract Deployment
The cost of deploying smart contracts has traditionally been one of the significant barriers for developers on the Ethereum network. High gas fees could make simple contract deployment or interaction costly, pushing developers to seek alternative solutions or blockchains.
Note
However, in 2024, the introduction of Layer-2 solutions and protocol upgrades like EIP-4844 have drastically cut these costs.
For instance, the cost of deploying a smart contract has dropped by nearly 40% compared to the pre-upgrade period. This cost reduction not only benefits the developers creating new dApps but also incentivizes those interacting with existing contracts. Projects like Uniswap and Aave—which handle numerous interactions with their contracts daily—have experienced tangible savings, making Ethereum a more attractive platform than ever.
This trend of reduced gas fees for smart contract deployment is driving a resurgence in Ethereum-based projects. Many developers who initially moved to alternative blockchains are now reconsidering Ethereum for its improved cost efficiency. The lowered transaction costs allow developers to experiment more frequently, launch iterative improvements, and deploy new features without the previous financial constraints.
Developer Reactions to Lower Gas Fees
The Ethereum community has responded enthusiastically to the reduced gas fees, leading to increased activity in smart contract deployments and a notable shift back to Ethereum from other blockchains. Many developers who had previously migrated to platforms like Solana or Binance Smart Chain are now finding Ethereum’s environment more financially viable.
Here’s a checklist of how developers have responded to the reduced transaction costs:
- Increased dApp deployments: More decentralized applications are being deployed on Ethereum due to lower deployment costs.
- More frequent use of smart contracts: Developers are engaging in frequent updates and interactions with smart contracts without the fear of prohibitive gas fees.
- Shifts back to Ethereum from other blockchains: Developers who left due to high costs are reconsidering Ethereum due to its improved economic feasibility.
Note
reactions are leading to a higher ETH burn rate, as more transactions are processed, although the reduced fees mean less ETH is burned per transaction. This balance between lower fees and increased transaction volume has allowed Ethereum to maintain its momentum, keeping the network active and engaging despite reduced costs.
How Lower Gas Fees Influence dApp and DeFi Activity
The sharp decline in Ethereum gas fees throughout 2024 has significantly impacted the decentralized application (dApp) and decentralized finance (DeFi) sectors. By reducing the cost of transactions, Ethereum has become a more accessible platform for both users and developers. This shift has not only encouraged the growth of new projects but also attracted users who were previously deterred by the high transaction costs. This section explores how lower gas fees are influencing the Ethereum ecosystem, particularly in DeFi protocols and dApp usage.
DeFi Protocol Activity and Lower Gas Fees
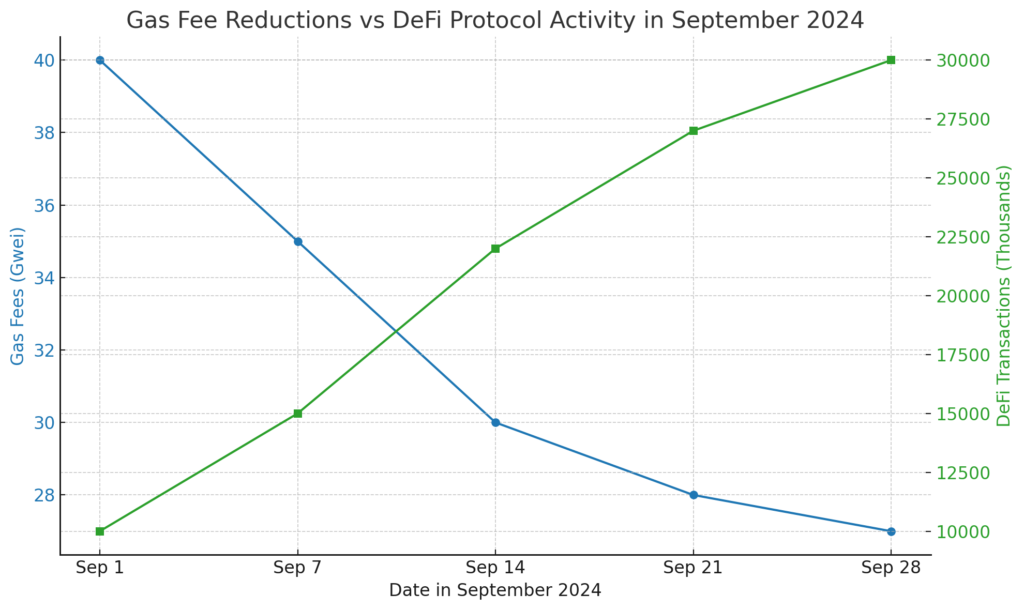
One of the most noticeable effects of reduced gas fees has been the surge in DeFi protocol activity. In the past, high transaction costs made staking, borrowing, and swapping on decentralized platforms expensive, limiting participation to wealthier users or those making large-scale transactions. Now, with gas fees averaging around 27.53 Gwei as of late September 2024, many DeFi protocols have seen a resurgence in user activity.
For instance, platforms like Aave, Compound, and Uniswap have reported increased engagement from users taking advantage of cheaper transaction costs. The reduced fees allow smaller transactions to be more viable, encouraging users to interact more frequently with DeFi products, including staking pools, liquidity provision, and decentralized exchanges (DEXs).
Reduced gas fees have been particularly impactful on swapping tokens within liquidity pools, where users can now trade tokens at a fraction of the previous cost. Lower gas fees are making DeFi more democratic, removing the financial barrier that kept many from engaging in complex DeFi strategies.
Increased User Adoption of dApps
The reduction in gas fees has also stimulated greater user adoption within the dApp ecosystem. Platforms requiring frequent transactions, such as NFT marketplaces and blockchain-based games, have benefited immensely from the reduced costs. For example, NFT minting fees, which once surged during high-traffic periods, are now more predictable and affordable. This change has made it easier for creators and collectors alike to engage with NFT platforms such as OpenSea and Rarible.
Blockchain gaming has also experienced a boom, with users flocking to platforms like Axie Infinity and Gods Unchained, where constant transactions are a key part of the gameplay. Reduced fees have allowed more casual users to participate without the fear of incurring high transaction costs. Additionally, dApp developers have taken advantage of these lowered fees to build more interactive applications, confident that users will not be deterred by prohibitive costs.
Note
spike in dApp usage is driving Ethereum network efficiency, as lower fees are encouraging more frequent, smaller transactions, which help distribute network load more evenly. The influx of users and developers has further solidified Ethereum’s role as the leading blockchain for decentralized applications.
Economic and Market Implications of Reduced Gas Fees

As Ethereum gas fees have significantly decreased in 2024, the broader economic effects on Ethereum’s market position and tokenomics have begun to emerge. While developers and users benefit from lower transaction costs, these changes have also impacted Ethereum’s deflationary model and influenced how traders and institutional investors perceive the network. This section will explore the economic ramifications of reduced gas fees on Ethereum’s ETH burn rate, market dynamics, and network scalability.
Effects on Ethereum’s Deflationary Model
Ethereum’s transition to a deflationary supply model, initiated by EIP-1559, relies on a portion of the gas fees being burned with every transaction. This mechanism removes ETH from circulation, thereby reducing the overall supply and making ETH more valuable over time. However, the current reduction in gas fees has led to fewer ETH being burned, slowing down the deflationary impact on the token’s supply.
For instance, before the recent upgrades, the Ethereum network would burn significant amounts of ETH during periods of high activity. In September 2024, with gas fees averaging around 27 Gwei, the burn rate has decreased. This slower burn rate means fewer ETH tokens are being permanently removed from circulation, which could affect long-term price appreciation and investor sentiment.
While the slower burn rate may temper Ethereum’s deflationary momentum, the lower transaction costs have incentivized increased transaction volume, partially balancing the deflationary effects. This trade-off has created a nuanced situation where Ethereum’s economic model continues to function, albeit at a different pace. Investors and users must now weigh the benefits of lower gas fees against the reduced deflationary pressure on the ETH supply.
Market Response to Lower Gas Fees
The broader cryptocurrency market, including both retail traders and institutional investors, has responded in varying ways to the reduction in Ethereum gas fees. Lower fees have generally been welcomed by the DeFi and dApp ecosystems, as they lower the barriers to entry for users and make Ethereum a more cost-effective platform for financial applications and gaming.
Institutional investors, in particular, are closely watching the shift in Ethereum’s cost structure. Reduced transaction costs enhance network scalability, allowing Ethereum to process more transactions without significant congestion, making it a more attractive investment for long-term growth. However, some investors may be concerned about the slower burn rate of ETH tokens, as this could dampen price appreciation in the short term.
For traders, lower gas fees have enabled more frequent transactions without the fear of incurring high costs, fostering greater market liquidity. The response from the wider market has been largely positive, with Ethereum maintaining its stronghold as the leading blockchain for decentralized finance and smart contracts despite these evolving dynamics. The expectation is that the September 2024 gas fee reductions will lead to increased network activity, further solidifying Ethereum’s position in the crypto market.
In September 2024, Ethereum’s gas fees have experienced significant changes, impacting various sectors within the Ethereum ecosystem. The reduction in gas fees, driven by Layer-2 solutions and network upgrades like EIP-4844, has benefited developers, users, and decentralized applications (dApps) alike. These lower fees have revitalized DeFi protocols and encouraged broader user adoption, particularly within NFT marketplaces and blockchain-based gaming platforms.
At the same time, the reduced gas fees have altered Ethereum’s deflationary model by slowing down the ETH burn rate, which in turn has nuanced effects on investor sentiment and the network’s economic model. However, the overall market response remains positive, with increased transaction volume making up for some of the slower deflationary pressure.
By keeping transaction costs low, Ethereum continues to maintain its dominance as a blockchain platform, while fostering innovation in dApp development and DeFi ecosystems. As these trends continue into the fourth quarter of 2024, Ethereum’s network efficiency and user engagement are expected to grow, solidifying its position in the broader crypto market.


















