The role of cryptocurrency in high inflation economies has gained considerable attention. As traditional fiat currencies face declining purchasing power due to inflation, cryptocurrencies have emerged as potential hedges and alternative investments. The growing importance of cryptocurrencies is evident in regions battling economic instability, where digital assets like Bitcoin and stablecoins are increasingly seen as viable stores of value. In these inflationary economies, crypto adoption rates have surged, driven by the need to preserve wealth and diversify investments. This trend highlights the evolving nature of cryptocurrencies in addressing the challenges posed by inflation, particularly in countries where economic uncertainty is prevalent.
Understanding Cryptocurrency’s Role in High Inflation Economies
High inflation can significantly erode the value of traditional fiat currencies, leading to a decline in purchasing power and savings. In response to this economic challenge, individuals and institutions often seek alternative stores of value. Cryptocurrencies have increasingly become a popular choice due to their potential to preserve wealth in inflationary environments. By providing an alternative to traditional investments, cryptocurrencies offer a new avenue for safeguarding assets amidst economic uncertainty, especially in regions experiencing high inflation.
Inflation’s Impact on Traditional Currencies
Inflation reduces the purchasing power of fiat currencies, causing the prices of goods and services to rise over time. When inflation rates soar, the value of savings in fiat money diminishes, prompting individuals and businesses to search for more stable stores of value. In extreme cases, such as hyperinflation, the devaluation of currency can be so severe that it leads to a loss of confidence in the national currency altogether.
For example, in countries like Venezuela, hyperinflation has caused the value of the national currency to plummet, leading citizens to turn to digital assets like Bitcoin as an alternative means of preserving their wealth. Similarly, in Argentina, high inflation has driven people to seek refuge in cryptocurrencies to avoid the devaluation of their savings. These scenarios highlight how inflationary pressures can force individuals and institutions to explore digital assets to protect their financial stability.
Inflation in traditional economies also leads to reduced consumer spending, as people hold off on purchases expecting prices to stabilize. However, this behavior can further slow economic growth, creating a vicious cycle of declining economic activity and rising prices. In contrast, the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies and their limited supply, especially with assets like Bitcoin, make them appealing as an alternative to fiat in inflationary markets.
Why Cryptocurrencies Are Considered a Hedge Against Inflation
Cryptocurrencies, particularly Bitcoin, are often viewed as a hedge against inflation due to their decentralized nature and finite supply. Bitcoin, with its capped supply of 21 million coins, is designed to mimic the stable inflation rate of gold. Unlike fiat currencies, which central banks can print in unlimited quantities, Bitcoin’s scarcity and predictable issuance rate make it less susceptible to inflationary pressures. This feature allows Bitcoin to retain its value over time, making it an attractive option for investors looking to hedge against the eroding value of fiat currencies.
Additionally, cryptocurrencies are not tied to any specific economy or central bank, making them less vulnerable to local economic and political turmoil. In times of economic instability, investors and institutions often flock to assets that are less influenced by government policies, and cryptocurrencies offer that level of independence. Moreover, the ability to transfer cryptocurrencies easily across borders adds to their appeal as a store of value in inflationary conditions, providing a hedge against inflation in economies where traditional financial systems may be failing.
Despite their volatility, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin have demonstrated resilience in times of economic crises, further cementing their role as a potential hedge. Investors may view these digital assets as a long-term store of value, particularly when facing high inflation rates and economic uncertainty.
Case Studies: Crypto Adoption in High Inflation Countries
Several high inflation economies have seen a surge in cryptocurrency adoption as citizens and institutions seek to preserve wealth and navigate economic instability. Two prominent examples are Venezuela and Argentina:
- Venezuela: Venezuela has been one of the most affected countries by hyperinflation, with its national currency, the Bolivar, experiencing extreme devaluation. In response, many Venezuelans have turned to cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to protect their savings. The ease of access to digital assets and the ability to bypass capital controls have made cryptocurrencies a vital tool for many citizens. According to reports, the use of Bitcoin in Venezuela has grown substantially, driven by the need to escape the country’s economic turmoil.
- Argentina: Similar to Venezuela, Argentina has faced high inflation rates for several years, leading to a significant loss in the value of the Argentine Peso. To counteract the economic instability, Argentinians have increasingly adopted cryptocurrencies as a store of value and a means of conducting transactions. The country’s citizens prefer cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and stablecoins, such as Tether (USDT), to mitigate the risk of further devaluation of their national currency.
| Country | Inflation Rate (2024) | Crypto Adoption Rate | Preferred Cryptocurrencies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Venezuela | Over 1,000% | High | Bitcoin, Dash, Tether (USDT) |
| Argentina | Around 115% | Growing | Bitcoin, Ethereum, Tether (USDT) |
*Note: The inflation rates mentioned are estimates as of 2024 and may vary based on economic conditions and data sources.
These case studies demonstrate how economic instability and high inflation drive the adoption of cryptocurrencies in countries with failing fiat systems. In such environments, digital assets offer a lifeline, providing an alternative means of storing value and conducting transactions without relying on unstable national currencies.
Inflation Rates in High Inflation Economies (2024):
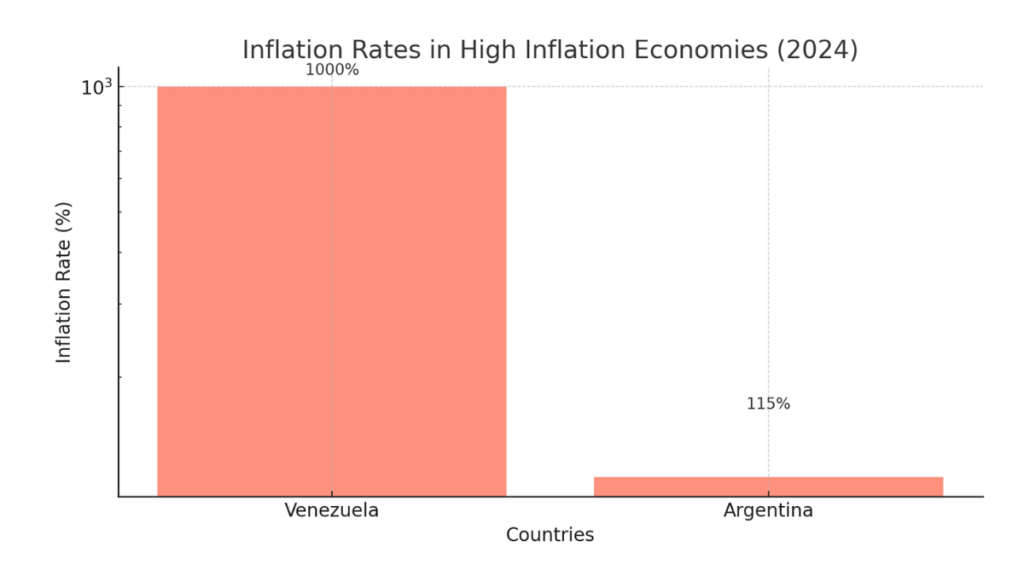
This chart uses a logarithmic scale to better illustrate the significant difference between the inflation rates in Venezuela and Argentina. Due to the vast difference in percentages (Venezuela’s rate being much higher), a logarithmic scale effectively displays this disparity.
Estimated Crypto Adoption Rates in High Inflation Economies (2024):
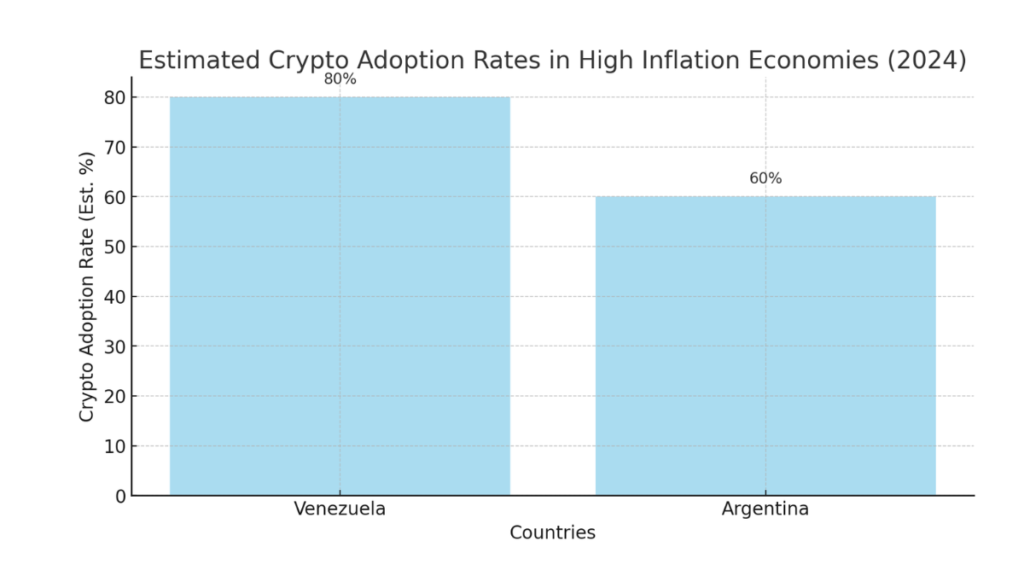
This chart shows the estimated crypto adoption rates in Venezuela and Argentina. While the exact percentages are approximations, the chart indicates high adoption in these countries, driven by their economic conditions.
Trends in Crypto Adoption Amid High Inflation
High inflation rates have been closely correlated with a surge in interest in digital assets. As traditional fiat currencies lose their value due to inflationary pressures, individuals and businesses in affected regions increasingly turn to cryptocurrencies as an alternative investment. In contrast to stable economies, where crypto adoption may be driven by different factors like technological innovation or investment diversification, high inflation economies see cryptocurrencies as a refuge from currency devaluation. This trend highlights the unique role that digital assets play in preserving wealth and financial stability amid economic turbulence.
Growth of Stablecoins in Inflation-Hit Regions
Stablecoins like Tether (USDT) have gained significant popularity in high-inflation economies due to their ability to maintain a stable value. Unlike other cryptocurrencies, which can experience high volatility, stablecoins are pegged to traditional assets such as the US dollar, providing a relatively steady digital equivalent of holding foreign currencies. This feature makes them especially attractive in countries experiencing severe inflation, where the local currency’s purchasing power is rapidly diminishing.
In regions like Latin America and Africa, where inflation rates have been particularly high, stablecoins have become a preferred means of storing value and conducting everyday transactions. For instance, Tether (USDT) allows individuals to hedge against the depreciation of their national currency without the need for complex financial instruments. By holding stablecoins, individuals can effectively protect their assets from local currency devaluation, facilitating cross-border transactions and remittances without the fear of losing value.
Moreover, stablecoins provide a level of financial inclusion in economies where access to banking services is limited. With a smartphone and internet access, individuals can store and transfer value securely, bypassing the traditional banking system. This capability is particularly beneficial in regions with economic instability, where trust in financial institutions may be low. As a result, stablecoins like USDT, USD Coin (USDC), and Binance USD (BUSD) have seen a marked increase in adoption rates in inflation-hit regions, serving as a digital shield against the ravages of inflation.
Impact of Inflation on Crypto Market Behavior
Inflation significantly influences cryptocurrency market behavior, especially in developing countries. As inflation rises, there is often an observable increase in trading volumes and a shift in investor preferences towards cryptocurrencies perceived as safe havens. In inflation-stricken economies, the devaluation of the national currency triggers a surge in demand for digital assets, which are seen as a more stable store of value.
Key Market Behaviors Influenced by Inflation:
- Increased Trading Volumes: High inflation typically leads to a spike in cryptocurrency trading activities, as individuals and institutions seek to quickly convert their depreciating fiat currency into digital assets.
- Preference for Stablecoins: Amid rising inflation, there is a noticeable preference for stablecoins over more volatile cryptocurrencies. Stablecoins like USDT are favored for their ability to maintain a consistent value, offering a safer hedge against the ongoing devaluation of fiat currencies.
- Shift from Traditional to Digital Assets: In high inflation economies, there is a growing shift from traditional assets like gold and real estate to digital assets. Cryptocurrencies offer a more accessible and liquid form of investment, enabling individuals to diversify their portfolios and protect their wealth.
- Increased Crypto Adoption for Daily Transactions: As inflation erodes the value of local currencies, cryptocurrencies become more commonly used for everyday transactions. This increased usage extends to remittances, payments, and savings, further embedding digital assets into the financial ecosystem.
These trends underscore the evolving dynamics of the cryptocurrency market in response to inflationary pressures. In developing countries, where economic instability is more pronounced, the move towards digital assets is driven not just by investment motives but also by the necessity to safeguard financial well-being. The rising inflation and subsequent crypto market behavior reflect a broader shift towards a decentralized financial system, where individuals have more control over their assets.
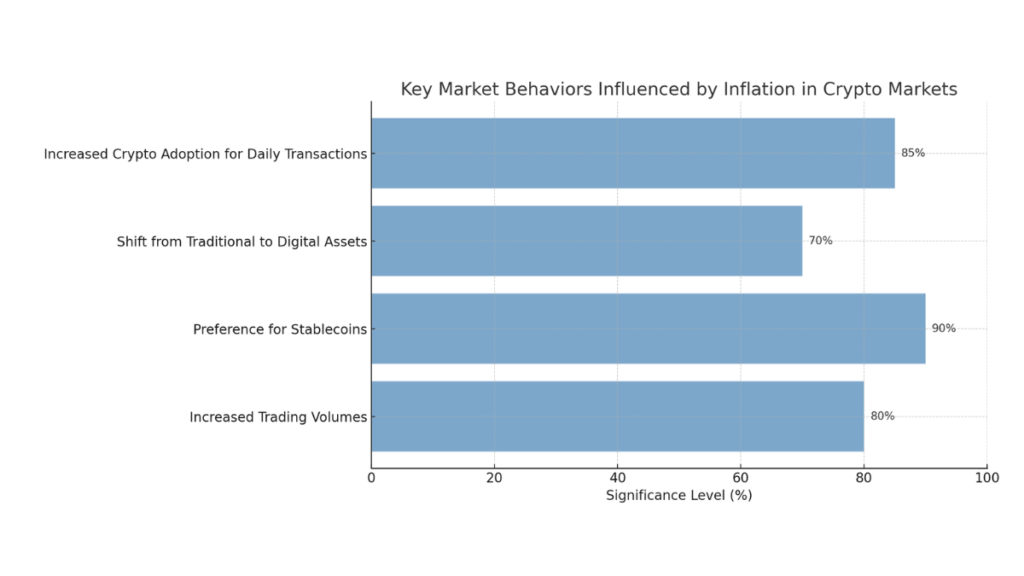
horizontal bar chart representing the key market behaviors influenced by inflation in crypto markets:
- Increased Trading Volumes
- Preference for Stablecoins
- Shift from Traditional to Digital Assets
- Increased Crypto Adoption for Daily Transactions
Risks and Challenges of Using Cryptocurrencies in High Inflation Economies
Cryptocurrencies have garnered attention as a potential hedge against inflation, particularly in economies experiencing high inflation rates. However, they come with inherent risks and challenges that can complicate their adoption. The primary concern is their market volatility, which can lead to unpredictable fluctuations in value. Additionally, regulatory hurdles and security issues present significant barriers to the widespread use of cryptocurrencies in these high-inflation contexts. Understanding these risks is crucial for individuals and institutions considering cryptocurrencies as a hedge in volatile economic environments.
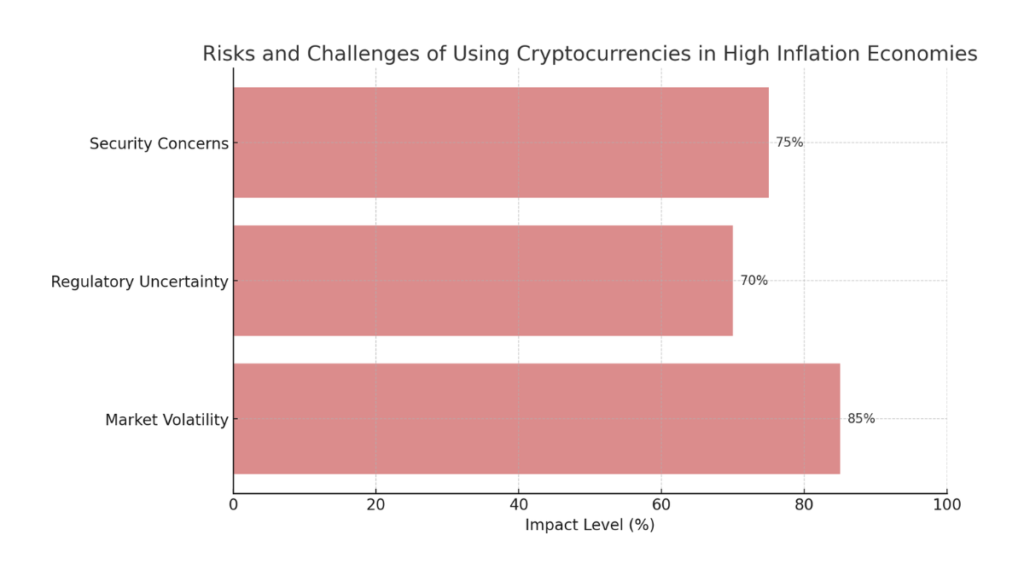
horizontal bar chart representing the risks and challenges of using cryptocurrencies:
- Market Volatility
- Regulatory Uncertainty
- Security Concerns
Volatility Concerns Amid Inflation Hedging
Cryptocurrency markets are known for their volatility, with prices often experiencing dramatic swings within short periods. While assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum have seen substantial gains over time, they have also been subject to sudden and severe market downturns. This volatility poses a significant challenge when considering cryptocurrencies as a hedge against inflation. Unlike stable assets such as gold or foreign currencies, cryptocurrencies can lose value rapidly, potentially negating their role as a reliable store of value.
For instance, during periods of global economic uncertainty, cryptocurrencies can exhibit even greater volatility, responding to changes in investor sentiment, market speculation, and macroeconomic trends. In high-inflation economies where individuals turn to cryptocurrencies to preserve their wealth, this volatility can result in further financial instability. The crypto market’s reaction to various factors—such as regulatory news, market trends, or technological advancements—can lead to significant price fluctuations, impacting the effectiveness of cryptocurrencies as a hedge against inflation.
Moreover, the correlation between traditional markets and cryptocurrencies has increased over the years. While cryptocurrencies were initially seen as independent assets, recent trends have shown that they can react similarly to traditional markets during periods of economic stress. This correlation diminishes their effectiveness as an inflation hedge, as their value may drop alongside other assets during economic downturns. Therefore, while cryptocurrencies can offer a refuge from currency devaluation, their inherent market volatility presents a risk that individuals and institutions must carefully consider.
Regulatory and Security Issues
Regulatory concerns are a significant challenge in the adoption of cryptocurrencies, especially in economies experiencing high inflation. Many governments and regulatory bodies are still in the process of developing frameworks to address the unique nature of digital currencies. This regulatory uncertainty can deter individuals and institutions from using cryptocurrencies as an inflation hedge. In some countries, strict regulations or outright bans on cryptocurrency trading and usage have been implemented, creating an environment of legal ambiguity. For instance, while some nations like El Salvador have embraced Bitcoin as legal tender, others have imposed strict controls on cryptocurrency transactions to maintain monetary stability and prevent capital flight.
Additionally, security concerns play a crucial role in the hesitance to adopt cryptocurrencies. The decentralized and digital nature of cryptocurrencies makes them vulnerable to hacking, fraud, and cyber-attacks. High-profile incidents such as exchange hacks and scams have resulted in significant financial losses for investors. In economies with failing fiat systems, where individuals might turn to digital currencies for protection, the risk of losing assets to security breaches can be a significant deterrent. Ensuring the safety of cryptocurrency holdings requires knowledge of secure storage methods, such as using hardware wallets and avoiding exposure on less reputable exchanges.
Another regulatory aspect involves the control of capital flows. In high-inflation economies, governments may impose capital controls to prevent the outflow of money and stabilize the currency. Cryptocurrencies can circumvent these controls, allowing individuals to move capital freely across borders. While this feature can benefit users seeking to preserve their wealth, it also raises concerns for governments trying to maintain economic stability. As a result, countries may enforce stricter regulations on cryptocurrency transactions, limiting their accessibility and usage.
In summary, while cryptocurrencies offer potential benefits as a hedge in high-inflation environments, their adoption comes with significant risks. Volatility, regulatory hurdles, and security concerns must be carefully weighed by those considering digital assets as an alternative to traditional financial instruments in inflation-hit regions.
The Future of Cryptocurrency in High Inflation Economies
As global economic changes continue to exert pressure on high-inflation economies, cryptocurrencies are poised to play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of financial systems. With traditional fiat currencies often struggling to maintain stability in such environments, digital currencies offer a promising alternative. The evolving landscape of cryptocurrency adoption in response to inflationary pressures indicates a shift toward more decentralized, secure, and accessible financial solutions. This shift is likely to redefine how financial systems operate, particularly in regions that face chronic inflation and economic uncertainty.
Integration of Cryptocurrencies into Mainstream Financial Systems
Cryptocurrencies are gradually moving towards integration into mainstream financial systems, especially in high-inflation countries where the need for alternative stable financial instruments is most acute. Several potential avenues for this integration could provide more stability and flexibility compared to traditional fiat systems:
- Crypto Payment Systems: Cryptocurrencies could be integrated into everyday payment systems, enabling users to conduct transactions seamlessly without relying on the volatile local currency. Merchants and consumers could use cryptocurrencies for goods and services, protecting themselves from rapid currency devaluation.
- Government-Backed Digital Currencies: Some high-inflation economies might consider issuing their own government-backed digital currencies, also known as Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs). These CBDCs could be designed to maintain a stable value, providing citizens with a secure digital alternative to cash that is less susceptible to inflationary pressures.
- Cross-Border Transaction Facilitation: Cryptocurrencies can streamline cross-border transactions, which is crucial in high-inflation economies where remittances form a significant part of the GDP. By adopting cryptocurrencies, countries can reduce transaction costs and increase the speed of cross-border payments, offering a more stable channel for transferring value.
- Decentralized Financial Services: Through decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, individuals can access lending, borrowing, and savings services without relying on traditional banks. This decentralization can offer financial services in high-inflation economies where banking infrastructure may be inadequate or untrustworthy.
Note
These integrations not only provide alternatives to the failing traditional systems but also promote financial inclusivity by enabling access to a broader range of financial services. As governments, businesses, and individuals explore these options, the role of cryptocurrencies in high-inflation economies is likely to become more pronounced.
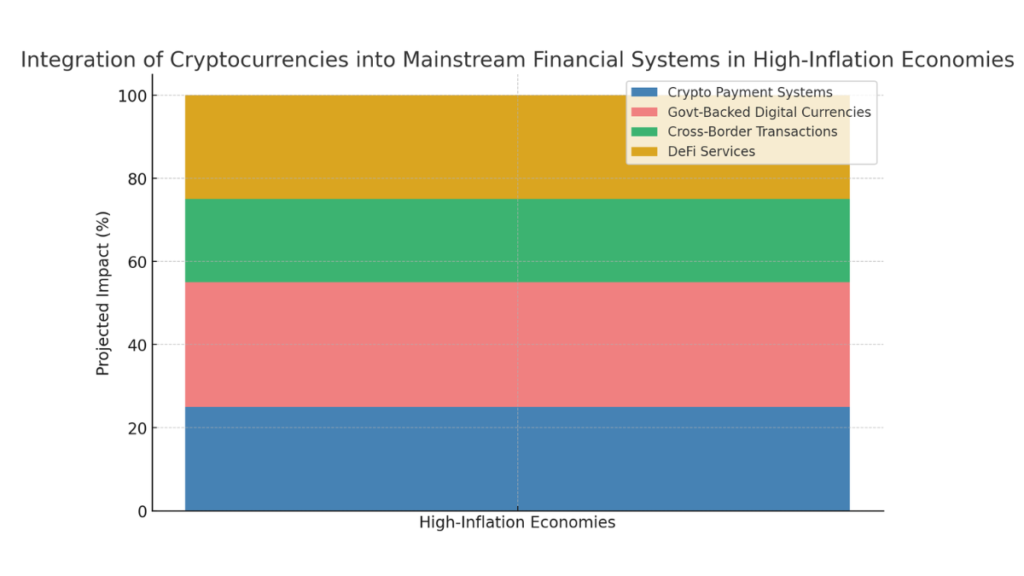
stacked bar chart representing the integration of cryptocurrencies into mainstream financial systems in high-inflation economies. Each section of the bar illustrates a different integration method:
- Crypto Payment Systems (25%)
- Government-Backed Digital Currencies (30%)
- Cross-Border Transactions (20%)
- Decentralized Financial Services (DeFi) (25%)
The Role of DeFi and Blockchain Technologies
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and blockchain technologies are at the forefront of the future financial landscape, especially in high-inflation economies. DeFi platforms offer a suite of financial services such as lending, borrowing, and asset management in a decentralized manner, bypassing the need for traditional intermediaries like banks. This is particularly advantageous in high-inflation countries where financial institutions may be unstable or inaccessible to the general population.
- DeFi in High Inflation Economies: DeFi platforms provide individuals in high-inflation economies with access to financial services that were previously out of reach. For example, users can lend their digital assets on DeFi platforms to earn interest, providing a hedge against the devaluation of their local currency. Additionally, DeFi platforms enable borrowing against crypto assets, allowing individuals to access liquidity without having to sell their holdings in an inflationary market. The transparent, secure, and accessible nature of DeFi services makes them an appealing option for those in regions facing economic instability.
- Blockchain Solutions for Inflation-Hit Regions: Blockchain technology underpins the operation of cryptocurrencies and DeFi platforms, offering a decentralized and immutable ledger for transactions. In high-inflation regions, blockchain can ensure transparency and security in financial transactions, reducing the risks associated with traditional banking systems. Moreover, blockchain facilitates the creation and management of stablecoins, which are crucial in providing a stable store of value in inflation-hit regions. By leveraging blockchain technology, these regions can establish more resilient financial infrastructures that are less prone to corruption, capital controls, and economic mismanagement.
The integration of DeFi and blockchain technologies into high-inflation economies has the potential to create a more secure, inclusive, and efficient financial ecosystem. It empowers individuals to take control of their financial assets, mitigating the adverse effects of inflation on their savings and investments. As these technologies continue to evolve, their role in shaping the financial systems of high-inflation economies is set to expand, offering innovative solutions to long-standing economic challenges.
Check the below Links
- Impact of US Inflation Data on Crypto
- Ethereum Market Performance
- Crypto Market Volatility Updates
- Current Bitcoin Price Trends
Cryptocurrencies are increasingly becoming a crucial component in high-inflation economies, offering alternative financial solutions to counteract currency devaluation. Their integration into mainstream financial systems and the rise of DeFi platforms signal a transformative shift in how individuals and institutions manage wealth in uncertain economic environments. Despite challenges like volatility and regulatory hurdles, the future points towards a more decentralized, accessible financial ecosystem where cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies play pivotal roles in enhancing economic resilience.



















