Cryptocurrency is a digital currency that uses blockchain technology to make transactions secure and decentralized. It is now vital to the global financial system because it allows transactions without traditional intermediaries like banks. Cryptocurrencies use cryptographic techniques to ensure security and privacy in digital transactions. To navigate today’s digital economy, you must understand cryptocurrency. Decentralized finance (DeFi) is becoming more important.
Understanding Cryptocurrency as Digital Currency
Not possible to remove the adverb. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are not like traditional money. Governments or central banks control traditional money. Cryptocurrencies use decentralized networks to manage transactions, relying on blockchain technology. This innovation has changed global finance. It enables secure, peer-to-peer transactions without banks or other intermediaries.
Definition and Basics of Cryptocurrency
At its core, cryptocurrency is a digital currency. It exists only in electronic form and works without a central authority. It runs on decentralized networks. Each participant verifies and records each transaction on a public ledger called the blockchain. This system uses cryptographic techniques to ensure security. They prevent fraud and protect user privacy. Cryptocurrencies have various uses. They can be an investment, a medium of exchange, or support decentralized apps (dApps).
Role of Blockchain in Cryptocurrency
Blockchain technology plays a critical role in supporting cryptocurrency transactions. It ensures transparency, security, and immutability. It records each transaction in blocks, which link in a chain. We have decentralized this system. It makes changing past transactions almost impossible. This reduces the risk of fraud.
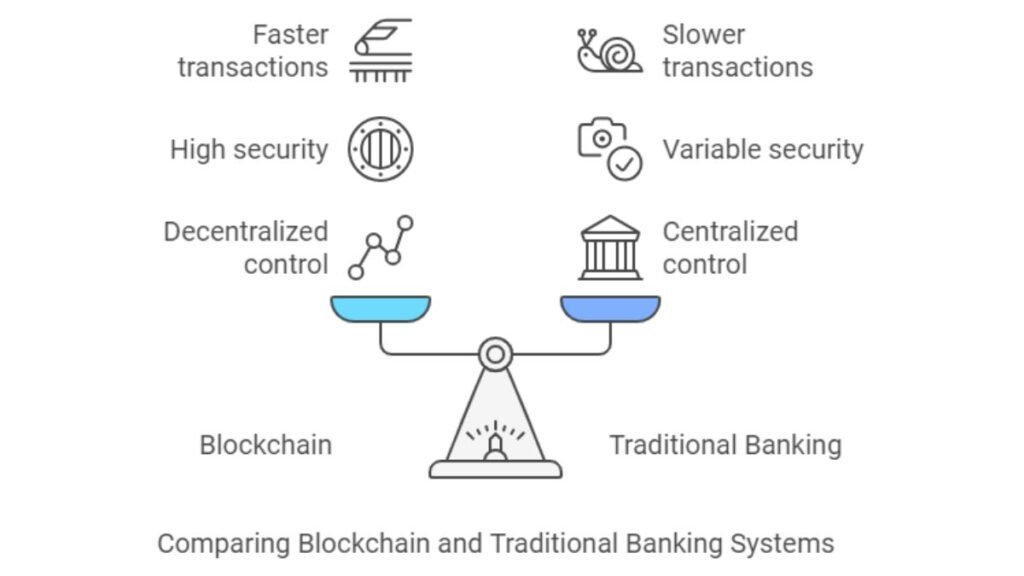
| Feature | Blockchain | Traditional Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Decentralization | Yes, managed by a network of nodes | Centralized control by banks |
| Security | High due to cryptography and immutability | Variable, reliant on security protocols |
| Transaction Speed | Typically faster, especially cross-border | Often slower, particularly for cross-border transactions |
| Intermediaries | None | Multiple (banks, payment processors) |
Cryptography’s Role in Securing Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency security relies on cryptographic techniques. They protect transaction integrity and ensure privacy. Each user has a pair of keys. A public key receives funds. A private key authorizes transactions. The private key is critical; if someone compromises it, the user can lose their funds. Cryptography also plays a role in creating digital signatures, which verify the authenticity of each transaction.
How Cryptocurrency Transactions Work
Cryptocurrency transactions use a decentralized system. This eliminates the need for banks as intermediaries. Unlike traditional banking, a central authority verifies its transactions. Cryptocurrency relies on a peer-to-peer network. Each participant records the transaction on a public ledger, the blockchain. It depends on the consensus mechanism used: Proof of Work or Proof of Stake. Either miners or validators confirm it. This process ensures transparency, security, and efficiency.
Peer-to-Peer Transactions
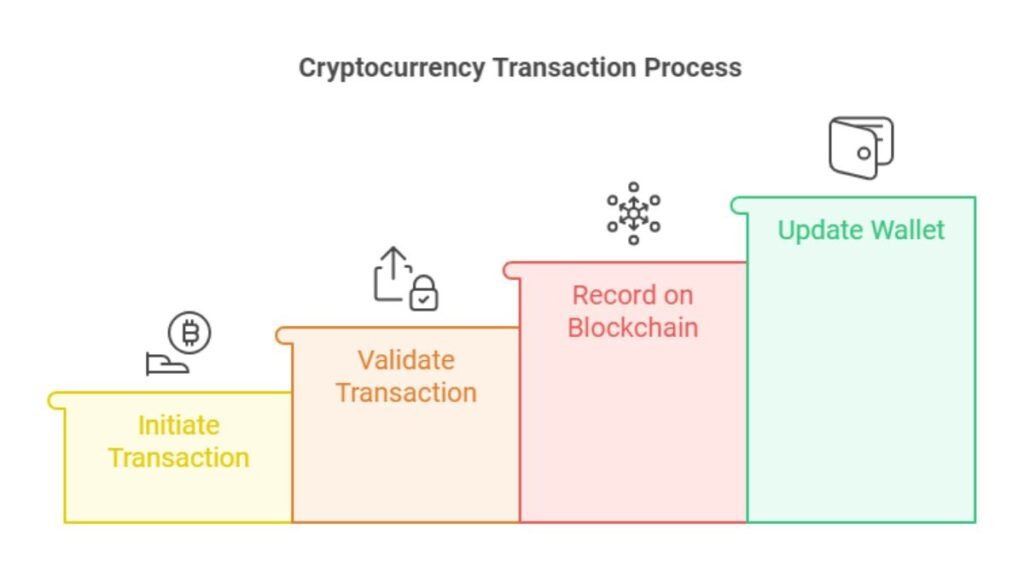
Peer-to-peer cryptocurrency transactions let users send and receive funds directly, without banks. These transactions are faster and cheaper than traditional banking. Their decentralized nature makes this possible. Here’s a simple breakdown of how it works:
- The sender initiates the transaction. They enter the recipient’s wallet address and the amount to send.
- The network, made up of nodes or validators, validates the transaction.
- The blockchain records the transaction. Once validated, the system adds it to a block. That block is then linked to the chain of previous transactions.
- The receiver gets the cryptocurrency. After the block is added to the blockchain, their wallet shows the new balance.
The Role of Miners and Validators
Cryptocurrency networks rely on miners (in Proof of Work) or validators (in Proof of Stake) to verify transactions and keep the network secure. In a Proof of Work system, miners compete to solve complex math problems. The first to solve it adds the next block to the blockchain. In return, they are rewarded with newly minted cryptocurrency.
In a Proof of Stake system, validators are chosen based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. This system is more energy-efficient than Proof of Work. It is used by networks like Ethereum since its transition to Ethereum 2.0.
Differences Between Public and Private Keys
Public and private keys are vital for crypto transactions. They ensure security and function. A public key is like a bank account number—it’s what you share with others to receive funds. , the private key is like a password that allows you to authorize transactions. You must keep the private key secure. If someone accesses it, they can control your cryptocurrency.
Different Types of Cryptocurrencies
The cryptocurrency landscape has evolved significantly since Bitcoin’s launch in 2009. Bitcoin is the most well-known cryptocurrency. But, there are now thousands of others. Each is for a specific purpose. For example, they can run decentralized apps or stabilize digital transactions.
Bitcoin: The First Cryptocurrency
Bitcoin (BTC) is the first decentralized digital currency. An anonymous entity, Satoshi Nakamoto, created it in 2009. It runs on a transparent blockchain. It is “digital gold,” a trusted store of value. Bitcoin’s peer-to-peer transactions remove the need for middlemen. This makes it a revolutionary force in finance. Bitcoin is the best-known cryptocurrency. Its security and adoption by institutions keep it on top of the market.
Ethereum and Smart Contracts
Ethereum (ETH) differs from Bitcoin. It introduced smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements coded onto the blockchain. Ethereum is more than a currency. It lets developers create decentralized applications (DApps). Ethereum recently switched to a Proof of Stake system. It is now more energy-efficient than Bitcoin’s Proof of Work system. This move cements Ethereum’s place in decentralized finance (DeFi).
Stablecoins and Their Role
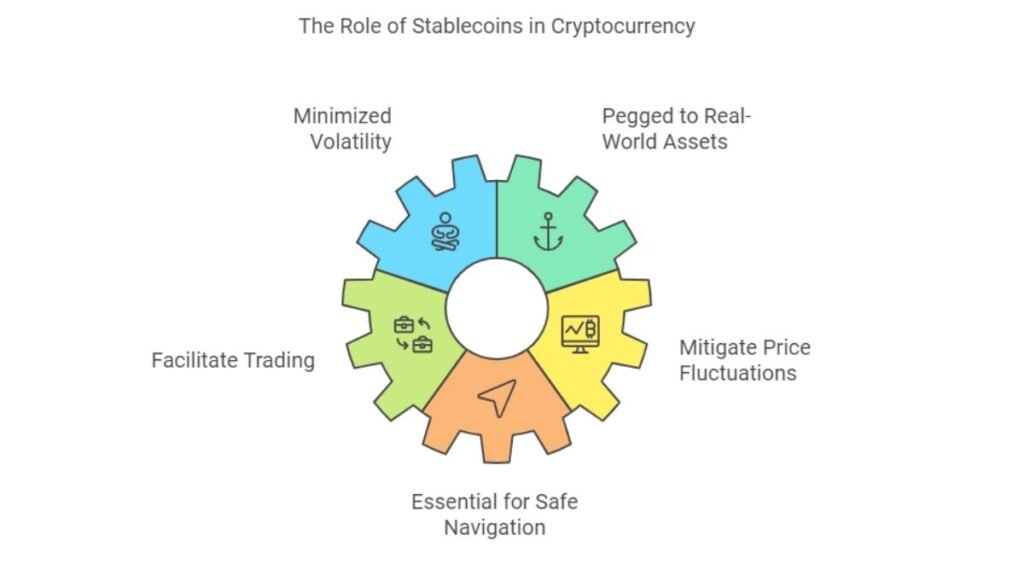
Stablecoins, like Tether (USDT), aim to reduce crypto volatility. They are pegged to real-world assets, like fiat currency. Tether ties itself to the US dollar, meaning 1 USDT aims to always equal 1 USD. Stablecoins are vital for trading and transacting with cryptocurrencies. They avoid the wild price swings of other digital currencies.
The Benefits and Risks of Using Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency offers unique opportunities in the financial world but also poses large risks. To make informed decisions, one must weigh both sides.
Benefits of Cryptocurrency
One of the most notable advantages of cryptocurrency is its decentralization. Cryptocurrencies run on blockchain networks. They don’t rely on central banks or governments like traditional currencies. This system removes the need for intermediaries, like banks. It cuts costs and makes cross-border payments more efficient. Often, cryptocurrency transactions are faster and cheaper, especially for international transfers.
Also, cryptocurrencies are globally accessible. They let people in areas with weak banks use online financial systems. This can significantly boost financial inclusion in developing economies. Additionally, security is a major benefit. Cryptographic methods make it hard to tamper with transactions on the blockchain.
Risks Associated with Cryptocurrency
Despite these benefits, cryptocurrencies come with significant risks. Volatility is one of the major concerns. Cryptocurrency prices, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, can change drastically in a short time. This makes them highly speculative investments. Another issue is the regulatory uncertainty that surrounds cryptocurrencies in various countries. Government actions, like bans in China, can harm digital assets. They may also make them hard to trade.
Note
Security is also a concern. Blockchain is secure. But hackers frequently target crypto exchanges and wallets. This has resulted in billions lost to cyber theft. Also, many cryptocurrencies have liquidity risks. It may be hard to convert them to cash in a short amount of time, especially for lesser-known coins.
How to Mitigate Cryptocurrency Risks
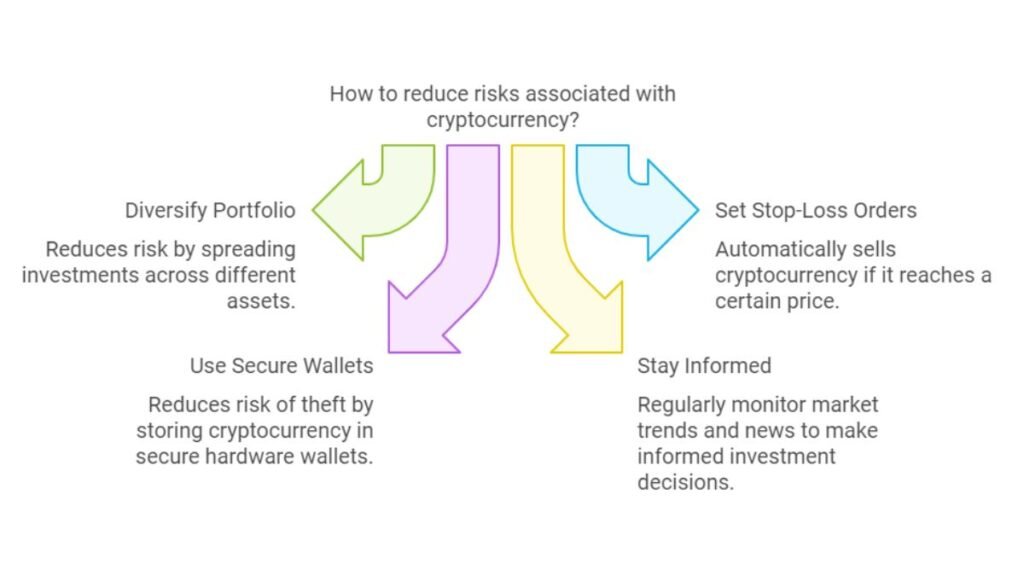
To cut the risks of cryptocurrency, you can use several strategies:
- Use cold storage wallets for long-term holdings. Offline hardware wallets are safer from hacks.
- Diversify cryptocurrency investments. Don’t put all your funds into one coin. Spread your investments across many assets. This reduces your risk.
- Stay updated on regulatory changes. Check local and global rules. This lets you expect legal risks and compliance issues.
- Use stop-loss strategies. Set points to sell an asset to limit losses in volatile times.
Future of Cryptocurrency in the Global Economy
Cryptocurrency will revolutionize global finance. It will create decentralized alternatives to traditional banks and change cross-border transactions. As more institutions adopt cryptocurrencies, their impact on finance grows. Many experts predict this shift will transform financial systems. It will improve access and decentralization. It will offer new tools and opportunities to those excluded from traditional banks.
Cryptocurrency and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platforms let users access financial services. These include lending, borrowing, and trading. Users do not need to rely on banks or other intermediaries. Cryptocurrency is crucial to DeFi. It uses blockchain technology to provide transparent, efficient, and borderless financial services. As DeFi evolves, we expect more innovative financial products. They will be driven by smart contracts and scalable blockchains. DeFi can democratize finance. It’s gaining traction. It attracts users seeking alternatives to traditional finance. This includes both individuals and institutions.
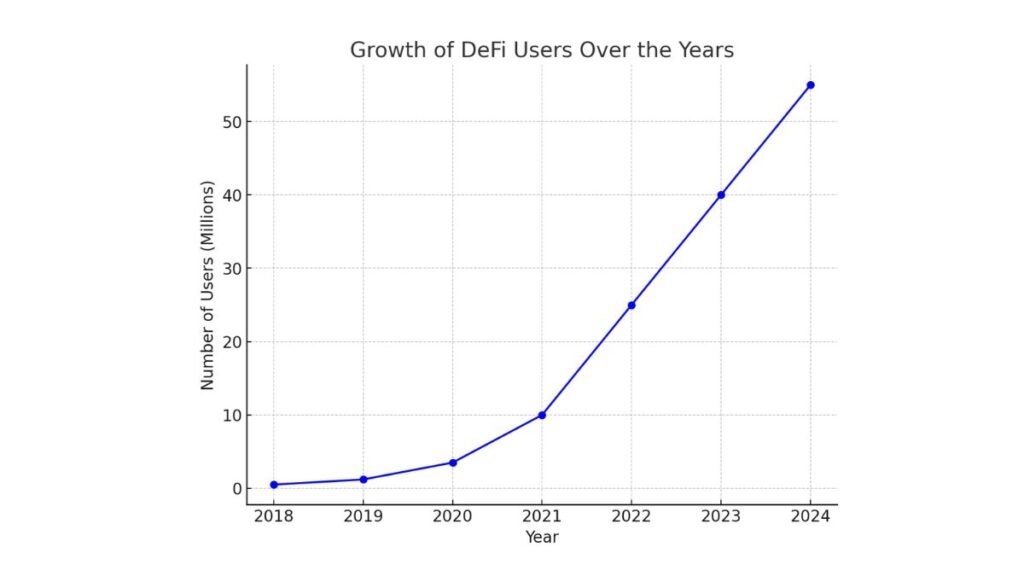
A line graph shows a sharp rise in DeFi users from 2018 to 2024. It reflects the growing popularity of decentralized finance platforms.
The Impact of Cryptocurrency on Traditional Financial Systems
Cryptocurrencies challenge traditional finance. They bypass central banks and intermediaries. They offer faster, cheaper transactions. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum have disrupted traditional banking. They provide peer-to-peer solutions without needing centralized control. As more institutions adopt crypto, the line between traditional finance and decentralized solutions may blur. This could reshape monetary policies and create new financial products.
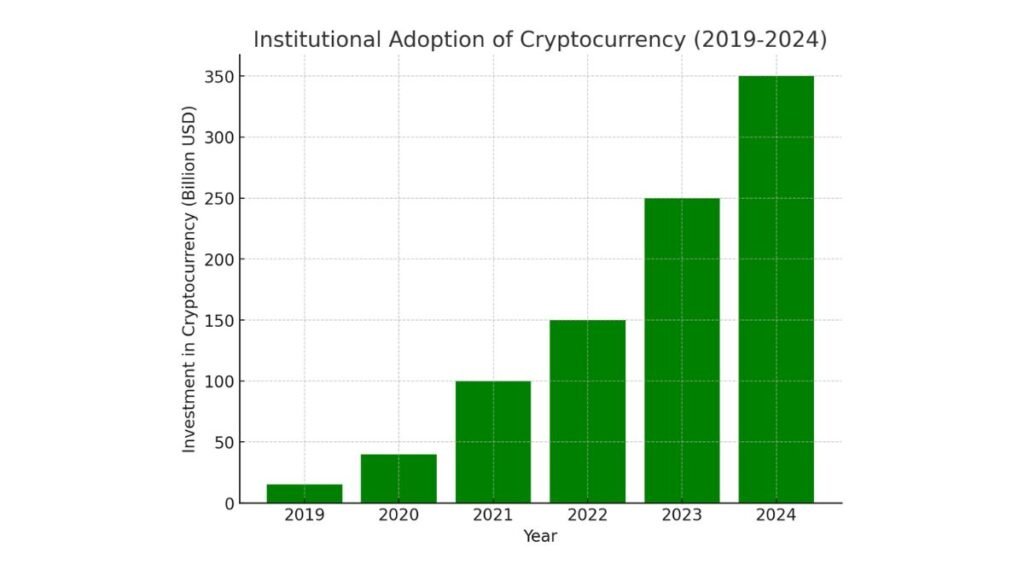
A bar chart shows the rise in institutional investment in crypto from 2019 to 2024. It highlights the significant capital flowing into the market.
The Role of Cryptocurrencies in Financial Inclusion
A key promise of cryptocurrencies is their potential to boost global financial inclusion. Over 1.7 billion people worldwide remain unbanked, primarily in developing countries. Cryptocurrencies give these populations access to vital financial services. They do not need traditional banks. Cryptocurrencies can eliminate geographic and bureaucratic barriers. They can empower individuals to join the global economy. This will boost growth and development in underserved areas.
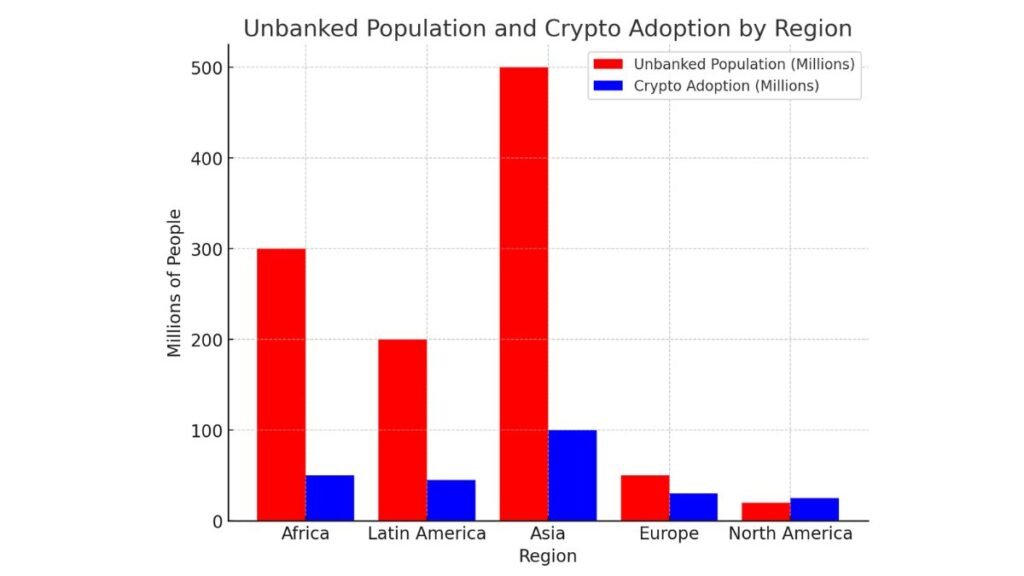
A bar chart compares the unbanked population to crypto adoption in different regions. It shows how cryptocurrency is improving financial inclusion, especially in developing areas.
Read More:
- What is Bitcoin and Why Does it Matter?
- How to Store Cryptocurrency Safely
- Ethereum 2.0 and Proof of Stake Explained
- Cryptocurrency Regulations and Compliance
- How to buy Bitcoin
Cryptocurrency is a key player in global finance. It offers both opportunities and challenges. It can enable decentralized finance, cut fees, and boost inclusion. So, it is a powerful tool for the future. But, investors and regulators must manage the risks. These include price volatility, regulatory uncertainty, and security concerns. In 2024 and beyond, DeFi, institutional adoption, and CBDCs will heavily impact crypto’s future.



















