In cryptocurrency, cryptographic security relies on the use of public and private keys to safeguard transactions and verify asset ownership. These keys play a crucial role in ensuring that only authorized individuals can access digital assets. The rise in key leaks and phishing attacks in 2024 highlights the growing need to secure private keys. Asymmetric encryption, which pairs public and private keys, is a fundamental component of blockchain security. It guarantees that transactions remain both transparent and secure. Following best practices for key generation, secure storage, and private key protection is more important than ever.
Understanding Public and Private Keys in Cryptography
Public and private keys are vital in cryptocurrency and blockchain. They form the core of asymmetric encryption, ensuring the integrity and security of cryptocurrency transactions. In asymmetric cryptography, each user has a public key and a private key. The public key is shared. The private key is kept secret. Together, these keys allow users to securely send, receive, and sign transactions. Public keys facilitate transparency, while private keys safeguard ownership and control over assets.
What is a Public Key?
A public key is a shared cryptographic string. It encrypts data and verifies digital signatures in blockchain transactions. When someone generates a public key, they pair it with a private key. The public key can be shared. It is used to create a public address, which lets users receive cryptocurrency. Public keys are accessible to anyone. They are secure. Only the holder of the private key can decrypt the information.
Public key cryptography is used in various blockchain applications. For instance, when someone sends funds, the transaction is encrypted with the recipient’s public key. This ensures that only the recipient, who holds the private key, can access the funds.
What is a Private Key?
A private key is a secret code. It gives its holder full control over the assets linked to the corresponding public key. The private key is vital for signing transactions. It verifies ownership and transfers funds in cryptocurrency. Keeping this key secure is crucial; if a private key is lost or stolen, the owner loses access to their cryptocurrency forever.
Private keys are typically stored in wallets, either online (hot wallets) or offline (cold wallets). While hot wallets are more convenient, they are more vulnerable to hacks. Cold wallets, on the other hand, offer stronger security by keeping private keys offline.
How Public and Private Keys Work Together
Public and private keys work in tandem to secure cryptocurrency transactions. When a transaction is initiated, it is signed using the private key, creating a digital signature. Anyone can verify this signature using the public key. It ensures the transaction’s authenticity and integrity. This process ensures that only the holder of the correct private key can authorize the transaction. It protects against fraud and tampering.
This system of encrypting data with a public key and decrypting it with a private key is the basis of cryptocurrency security. They enable trustless transactions. Only authorized users can control assets on the blockchain.
The Role of Public and Private Keys in Blockchain Transactions
In blockchain transactions, public and private keys are crucial for ensuring security and verifying the authenticity of transactions. The private key is a digital signature, authorizing each transaction. The public key lets others verify its validity. These keys work together to maintain trust and security in a decentralized system where no central authority oversees transactions.
Signing Cryptocurrency Transactions with Private Keys
A private key is used to sign cryptocurrency transactions, confirming that the person initiating the transaction is the legitimate owner of the associated funds. A transaction uses your private key to create a digital signature. It proves your ownership and authorization without exposing the key. Once signed, this transaction is broadcasted to the blockchain network for validation by nodes.
For secure transactions, it is critical to protect private keys from exposure or theft. Here are best practices:
- Always keep private keys offline (use cold storage solutions like hardware wallets).
- Use hardware wallets for added security, which store your private keys on a physical device.
- Backup your private keys in multiple secure locations (preferably encrypted or in physical form).
Note
If you fail to protect your private key, someone could access your cryptocurrency. Once a private key is compromised, you can’t reverse the transaction or recover the funds.
Verifying Transactions with Public Keys
The public key is used to verify the authenticity of a signed transaction. When a transaction is broadcasted to the blockchain, the public key allows validators to confirm that the transaction was indeed signed by the corresponding private key holder. This ensures the integrity and authenticity of the transaction without exposing sensitive information.
The public key also helps confirm that the transaction has not been tampered with during the process. This step is vital to keeping blockchain networks decentralized and trustless. It prevents unauthorized users from manipulating the blockchain.
Key Generation and Security Best Practices
In the world of cryptocurrency, key generation is vital for ensuring the security of digital transactions. Complex cryptographic algorithms generate public and private key pairs. This creates a strong system for securing data and verifying transactions. To prevent theft or unauthorized access, it’s vital to use strong keys and protect them.
Generating Public and Private Key Pairs
Public and private key pairs are commonly generated using cryptographic algorithms like Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) and RSA. Both methods create secure keys that are nearly impossible to reverse-engineer.
- Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC): ECC has become a popular choice in blockchain due to its ability to provide strong security with smaller key sizes compared to RSA. For example, a 256-bit ECC key provides the same level of security as a 3072-bit RSA key. This efficiency makes ECC ideal for environments with limited processing power, such as mobile devices or IoT networks. ECC generates a private key as a random integer and a public key from points on an elliptic curve.
- RSA: RSA key generation is based on the difficulty of factoring large prime numbers. It’s still widely used but requires much larger key sizes to offer the same security as ECC.
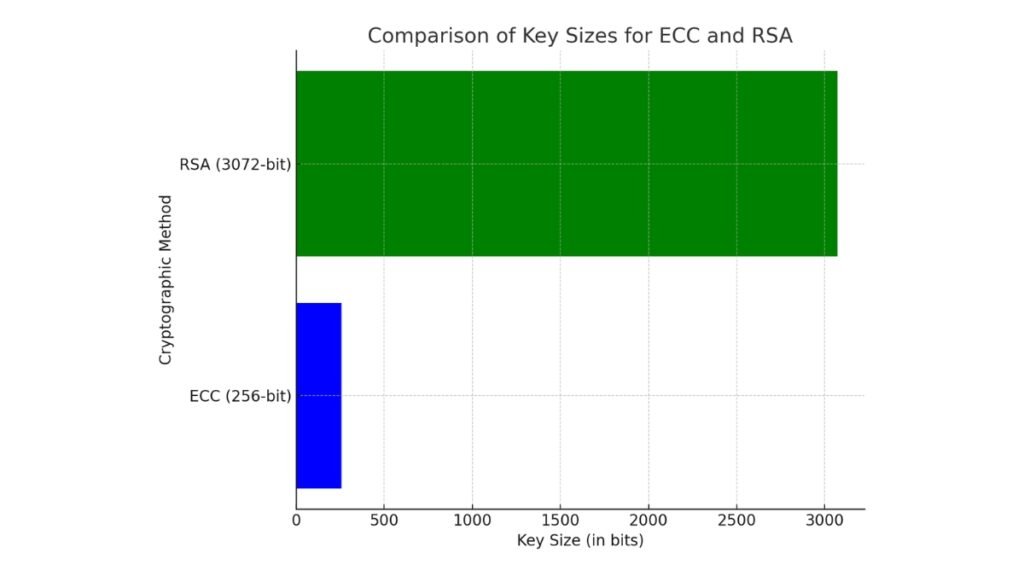
The bar chart above compares the key sizes required for equivalent security levels between Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) and RSA. ECC provides the same level of security as RSA with significantly smaller key sizes, highlighting its efficiency for environments.
Note
The process involves selecting a curve and a base point for ECC, or large prime numbers for RSA. Wallets use cryptographic methods to create secure key pairs. They are essential for managing blockchain transactions and ensuring data integrity.
Safeguarding Private Keys
Once keys are generated, safeguarding private keys becomes the top priority. If a private key is exposed or lost, the associated funds can be permanently lost. Below are best practices for protecting private keys:
- Store keys in hardware wallets: Hardware wallets keep private keys offline, making them far less vulnerable to hacking. This “cold storage” method is highly recommended for long-term holders.
- Backup seed phrases in multiple locations: A seed phrase can regenerate a private key if it’s lost. Ensure these backups are stored in secure places, such as encrypted storage or physical safes.
- Use two-factor authentication (2FA): It adds security to your wallet. If a password is compromised, it prevents unauthorized access.
Avoiding Common Key Management Mistakes
Managing private keys correctly is critical in cryptocurrency security. Losing or exposing your private keys can lead to irreversible loss of funds. Effective key management prevents this from happening and ensures the safe handling of your assets. Let’s explore some common mistakes and how to avoid them.
Avoiding Private Key Exposure
Exposing your private key can let others access your crypto. You may lose your funds. To reduce these risks, keep your private key secret. Use strong security practices. Here’s how to avoid key exposure:
- Avoid storing private keys online: Never store your private key in cloud storage or easily accessible locations. Hackers frequently target online storage, making it unsafe for sensitive information.
- Do not share your private key: Always keep your private key secret, even from people claiming to offer support services. If anyone else gains access, they can take control of your assets.
- Use hardware wallets: Store your private keys offline using a hardware wallet. This keeps them out of reach from malware and hackers.
Backup and Recovery Solutions for Private Keys
Properly backing up your private keys is essential to prevent losing access to your funds in case of device loss or failure. Here are best practices to secure your private keys:
- Use seed phrases: When setting up a wallet, you’ll generate a seed phrase that acts as a backup for all your private keys. Store this seed phrase in multiple secure locations to ensure you can recover your funds if needed.
- Consider encrypted backups: If you prefer digital storage, ensure your backup is encrypted. Storing backups on external hard drives or in a password-protected vault can also add layers of security.
- Regularly update and test backups: Keeping your backups updated is crucial, especially when moving funds or changing wallets. Additionally, periodically test your backups to ensure they work when needed.
This chart shows best practices for backing up private keys. It stresses using seed phrases, encrypted backups, and regularly updating and testing them.
Read suggested articles
- Crypto Wallet Security Best Practices
- Introduction to Blockchain Cryptography
- How to Set Up a Secure Hardware Wallet
- Elliptic Curve Cryptography in Blockchain
- Common Cryptocurrency Scams and How to Avoid Them
It’s vital for anyone in cryptocurrency to know about public and private keys. These tools secure transactions. They verify ownership and ensure data integrity. Key generation using methods like ECC boosts security and efficiency. Use strong security measures. They protect your assets from cyber threats and human error. This includes hardware wallets and encrypted backups. Ultimately, proper key management is the cornerstone of protecting your digital wealth.



















