It’s more important than ever to secure crypto transactions for new users. Digital currencies pose new risks, and users can reduce losses by following security best practices. This guide provides step-by-step, safe methods for using the blockchain. It covers initiating, verifying, and completing transactions. It emphasizes key elements like wallet addresses, transaction fees, and confirmations. With secure practices, you can protect your assets from fraud or errors.
Setting Up a Cryptocurrency Wallet for Transactions
Before initiating any cryptocurrency transactions, having a secure wallet is essential. A wallet allows you to store, send, and receive cryptocurrencies. In this section, we will explore the types of wallets available, their setup processes, and the importance of securing private keys. New to crypto or an experienced user? Choose the right wallet and follow security best practices. They keep your assets safe.
Choosing Between Hot and Cold Wallets
When setting up a crypto wallet, it’s crucial to know the difference between hot and cold wallets.
- Hot Wallets: These wallets are connected to the internet, making them ideal for frequent transactions and easy access. They come in the form of mobile apps, web-based platforms, or desktop software. However, because they are always online, they are more vulnerable to hacks and cyber-attacks. Hot wallets are suitable for users who need instant access to their crypto for trading or daily use.
- Cold Wallets: Cold wallets are offline and are considered much more secure since they aren’t exposed to the internet. These wallets come in hardware forms like Ledger or Trezor and are ideal for long-term holders or those with significant amounts of cryptocurrency. Cold wallets significantly reduce the risk of online attacks but can be less convenient for frequent transactions.
When choosing between these wallets, it’s important to consider how often you plan to access your cryptocurrency. For frequent transactions, hot wallets offer convenience, but for long-term storage, cold wallets provide stronger security.
Safeguarding Your Private Keys
Your private keys are the most important element of your cryptocurrency wallet. They provide access to your funds and should be protected at all costs.
- Online vs. Offline Key Storage: Storing private keys online, such as in cloud storage or on your personal computer, increases the risk of hacks. It’s safer to store them offline, either on a physical device or written down and stored in a secure location.
- Use of Hardware Wallets: A hardware wallet keeps private keys offline, offering the highest level of security. These devices never connect to the internet and require physical access to authorize any transaction.
To ensure the utmost security, avoid sharing your private keys with anyone and never enter them on any online platform.
Backing Up Your Seed Phrase
When you create a cryptocurrency wallet, you’re given a seed phrase (usually 12 to 24 words). This phrase is critical for recovering your wallet if your device is lost or damaged.
- Avoid Digital Storage: Never store your seed phrase on a digital device like a computer or smartphone. Digital storage methods can be compromised by malware or hackers. Instead, write it down on paper.
- Multiple Backups: Keep multiple physical copies of your seed phrase in secure locations, such as a safe deposit box or a trusted family member’s care. Some users even engrave their seed phrase on metal plates to ensure durability and resistance to damage.
By taking these steps, you ensure that even in the worst-case scenario, your wallet and funds can be recovered.
Executing a Cryptocurrency Transaction
Sending cryptocurrency to another wallet address is a key function for any crypto user. In this section, we’ll explore how to execute secure transactions by correctly entering wallet addresses, adjusting network fees, and understanding blockchain confirmations to ensure a smooth and safe transfer process.
Entering the Correct Wallet Address
Entering the correct wallet address is the most critical part of any cryptocurrency transaction. Unlike traditional bank transfers, crypto transactions are irreversible. If you send funds to the wrong address, you won’t be able to recover them. This makes it essential to double-check the address before confirming a transaction.
- Select the cryptocurrency:
- Choose the coin type from the dropdown menu. Example: Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), etc.
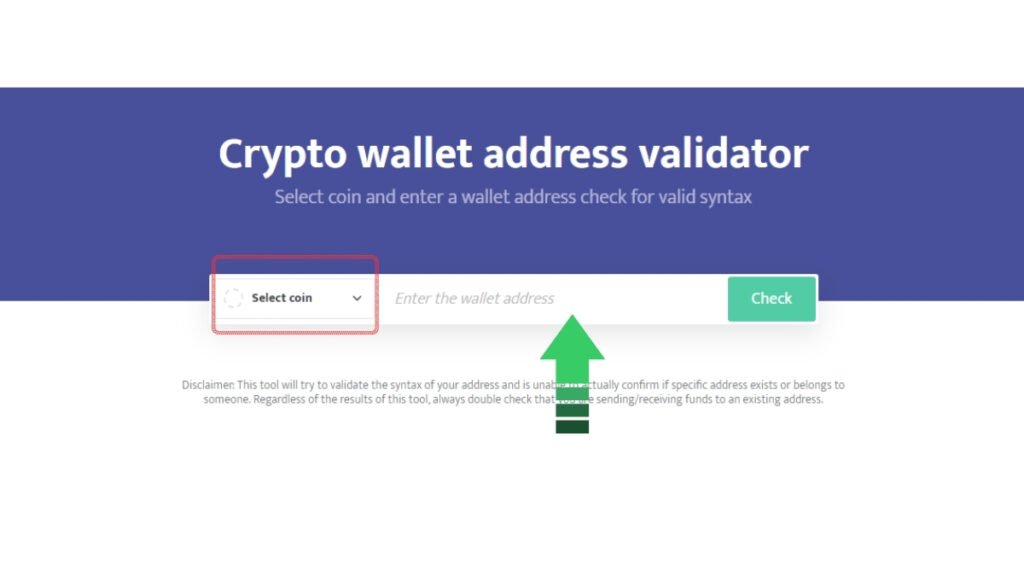
- Enter the wallet address:
- Paste or type the wallet address you wish to validate in the input box next to the selected coin.
- Click on the “Check” button:
- After entering the wallet address, click on the “Check” button to initiate the validation process.
- Validation outcome:
- If the wallet address format is correct and meets the necessary criteria, the system will return a message like: “Wallet address syntax looks valid.”
- If the wallet address has issues or an incorrect format, you will get a message like: “Wallet address syntax looks invalid.”
- Common mistakes to avoid:
- Do not use private wallet addresses for mining (e.g., private Ethereum addresses that start with 0x but are 62 characters long).
- Ensure you are using the correct coin address (e.g., don’t use a Bitcoin address for an Ethereum pool).
- Avoid using random or incorrect wallet addresses or those that contain special characters.
- Critical final check:
- Always remember that this tool only checks the syntax (format) of the address. It doesn’t verify ownership or the existence of the wallet. Always double-check the accuracy of the address before sending or receiving any coins.

Setting Network Fees for Transactions
Network fees, also known as gas fees on networks like Ethereum, are small amounts paid to incentivize miners or validators to process transactions. These fees vary depending on the blockchain and current network traffic.
- How Fees Work: Each blockchain has its own method of calculating fees. For example, Ethereum uses gas fees which fluctuate based on the complexity of the transaction and network congestion. Bitcoin also has variable transaction fees, with users able to set higher fees for faster confirmations.
- Adjusting Fees for Speed: If you need a transaction to be processed quickly, you may opt to pay higher fees. Most wallets provide a choice between “slow,” “average,” and “fast” processing speeds. Faster speeds come with higher fees, while slower transactions may cost less.
| Blockchain | Average Network Fee (USD) |
|---|---|
| Bitcoin | $2 – $20 (depends on speed) |
| Ethereum | $5 – $50 (varies with gas fees) |
| Binance Smart Chain | $0.10 – $0.50 |
Adjusting your transaction speed can help you control costs, especially during high network activity.

Understanding Blockchain Confirmations
Once you’ve submitted a transaction, it must be confirmed by the blockchain. Blockchain confirmations verify that the transaction is legitimate and ensure it’s permanently added to the blockchain ledger.
- What is a Confirmation?: A blockchain confirmation occurs when a network node processes a transaction and includes it in a block. Depending on the network, multiple confirmations may be required before the transaction is fully completed.
- Confirmation Time: The number of confirmations needed and the time it takes depends on the blockchain. Bitcoin transactions may require six confirmations, which could take around an hour, while Ethereum typically requires fewer confirmations for faster processing.
- Checking Confirmation Status: To verify your transaction’s progress, you can use a blockchain explorer like Etherscan or Blockchair. These tools allow you to enter your transaction hash to view details like confirmation status, transaction time, and associated fees.
Verifying and Tracking Transactions on the Blockchain
After submitting a cryptocurrency transaction, it’s essential to track and verify its progress. Blockchain explorers are powerful tools that allow users to check the transaction’s status, ensuring it is securely recorded on the blockchain. By using these tools, you can confirm details like the transaction hash, network fees, and wallet balances to prevent any issues.
Using Blockchain Explorer Tools
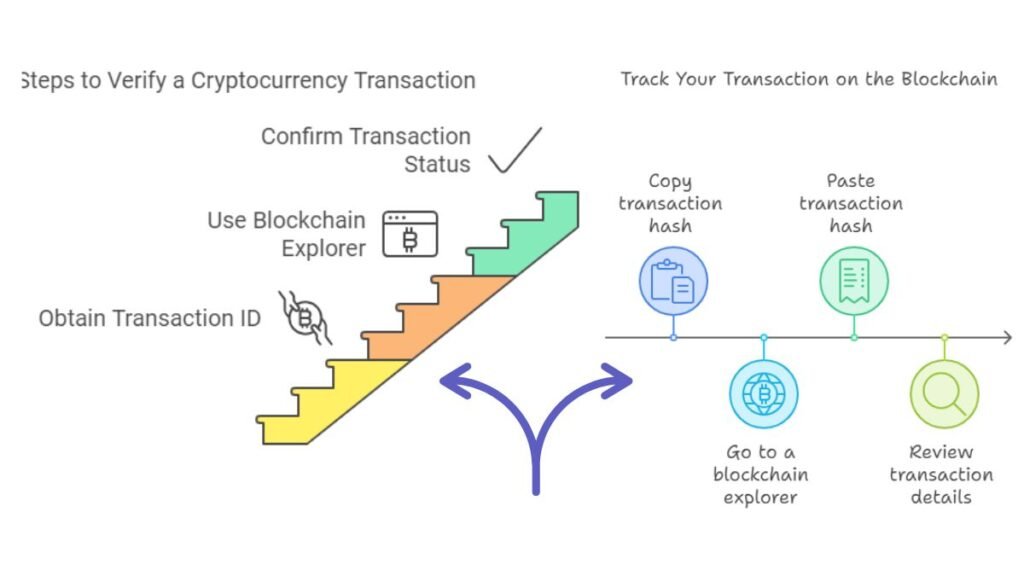
Blockchain explorers, such as Etherscan (for Ethereum) or Blockchair (for multiple networks), allow users to track their transaction’s progress in real-time.
- How Blockchain Explorers Work: These platforms display data directly from the blockchain, showing you details like the transaction hash, number of confirmations, sender and receiver addresses, and fees paid. This allows you to verify whether your transaction has been successfully processed or if there are any delays.
- The Importance of Transaction Hash: Every transaction on the blockchain generates a unique transaction hash. Think of this as a digital receipt. By entering this hash into a blockchain explorer, you can access all the details of your transaction. The hash is crucial for verifying that your transaction is being processed correctly.
Steps to Verify a Transaction:
- Copy the transaction hash from your wallet or exchange.
- Go to a blockchain explorer (e.g., Etherscan for Ethereum).
- Paste the transaction hash into the search bar and click enter.
- Review the transaction status, number of confirmations, and other relevant details.
Note
By verifying the transaction, you ensure that your cryptocurrency transfer is progressing as expected, and you can take action if anything looks wrong.
Monitoring Transaction History
After verifying a single transaction, it’s also useful to monitor your transaction history to keep track of all your blockchain activity.
- Checking Transaction Statuses: Once you submit a transaction, it may show as “pending” until the network processes it. After receiving sufficient confirmations, the status will change to “completed” or “confirmed.” Each blockchain has different confirmation requirements. For example, Bitcoin transactions typically need six confirmations, while Ethereum may need fewer.
- Interpreting Pending vs. Completed:
- Pending: This means the transaction is still being processed by the network. You may experience longer wait times during periods of high traffic.
- Completed: Once enough nodes in the network confirm the transaction, it is permanently recorded on the blockchain and considered final.
Monitoring your transaction history is vital to ensure every transfer is properly documented, especially for large amounts or multiple transfers. Blockchain explorers make it easy to search your entire transaction history, giving you peace of mind that your funds are moving as intended.
Securing Transactions with Additional Safety Measures
When making cryptocurrency transactions, security should be your top priority. By using best practices like two-factor authentication (2FA) and VPNs, you can significantly reduce the risk of fraud or unauthorized access to your assets. This section will cover these key safety measures and how they help protect your crypto transactions.
Enabling Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds security. It requires two forms of ID to access accounts. This security method combines something you know (like a password) with something you have (like a mobile authentication app). For better security, use app-based authenticators, like Google Authenticator or Authy. They generate time-sensitive, one-time codes that hackers can’t easily intercept. Hardware tokens (like YubiKeys) offer an even stronger security option. These physical devices generate unique codes, adding an extra barrier to unauthorized access.
2FA greatly lowers the risk of account compromise. It protects your crypto transfers from unauthorized logins, even if your password is stolen.
Using a VPN for Secure Connections
Using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) ensures that your internet connection is secure while making cryptocurrency transactions. VPNs encrypt your data, hiding your IP address and safeguarding your personal information from hackers. This is especially critical when using public Wi-Fi, which can be exploited by cybercriminals to intercept unprotected data.
A VPN protects you by routing your traffic through encrypted servers. This prevents anyone from monitoring your online activities. This is vital for keeping your transactions private and secure. It reduces the risk of phishing and man-in-the-middle attacks.
Avoiding Phishing Scams
Phishing scams are one of the most common tactics used by hackers to steal cryptocurrency. Scammers often send fake emails or create fake websites. They appear legitimate and trick users into giving their private keys or login info. To protect against these scams, it’s essential to verify the legitimacy of the websites and emails you interact with.

- Never share your private keys: Your private keys should never be shared with anyone or entered on any website.
- Double-check URLs: Before entering sensitive info, ensure the URL is correct. The site should have a valid SSL certificate (indicated by “https”).
- Use an anti-phishing code. Some exchanges offer this feature. It lets you set a unique code that will appear in all legitimate emails from the exchange.
Note
By staying vigilant and recognizing the signs of phishing, you can protect your cryptocurrency from theft.
Preventing and Troubleshooting Transaction Errors
Cryptocurrency transactions can sometimes fail. This can cause delays or lost funds. By understanding these common issues and how to troubleshoot them, you can ensure a smoother transaction process.
Common Transaction Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Several common errors can occur when making cryptocurrency transactions. Here’s a checklist of the most frequent mistakes and how to prevent them:
- Double-check the wallet address: One of the most critical errors is sending crypto to the wrong wallet address. Crypto transactions are irreversible. So, always double-check the wallet address to avoid mistakes.
- Ensure enough funds for fees: Another frequent issue is insufficient funds. You must ensure that your wallet contains enough funds not just for the transaction but also to cover the network fees.
- Select a transaction speed. Choose a fee based on how fast you want to process it. Higher fees can speed up the process, while lower fees might cause delays.
- Verify network status: If the blockchain is congested, transactions may be delayed or fail. Before sending, check the network’s status on Etherscan. It shows congestion levels.
Troubleshooting Delayed Transactions
Delayed transactions are often due to network congestion. It happens when the number of transactions exceeds the blockchain’s capacity. Here are some solutions to help you address delays:
- Increase transaction fees: If your transaction is taking too long to confirm, you can increase the fee. Use methods like Replace by Fee (RBF). It lets you replace an unconfirmed transaction with a higher fee to ensure miners prioritize it.
- Check mempool size. High network activity can grow the mempool (unconfirmed transactions). This may slow confirmations. Using tools like blockchain explorers, you can check the mempool size and decide whether to wait or adjust your fee.
- Use transaction accelerators: Some mining pools offer services to accelerate stuck transactions. By submitting your transaction to an accelerator, you may expedite its confirmation.
By knowing these issues and their solutions, you can avoid or fix most crypto transfer errors.
Dive Deeper:
- Using exchanges securely
- Protecting Your Crypto Assets
- Introduction to Blockchain Technology
- Yield Farming for Beginners
- Evaluating slippage in crypto trades
Secure crypto transactions require diligence. You must choose the right wallet and verify blockchain confirmations. Knowing common transaction errors and how to fix them helps ensure smooth, reliable transfers. Use safety measures, like two-factor authentication and VPNs, to better protect your digital assets. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and use these best practices. They will secure your crypto transactions in a changing digital world.



















