NFTs, or Non-Fungible Tokens, are now key in the digital asset world. They have changed how we view online ownership. A Beginner’s Guide to NFTs will explain their core concept. NFTs are digital assets that are unique and stored on blockchains like Ethereum or Solana. NFTs have many uses. They include digital art, virtual real estate, and collectibles. NFTs are key to digital ownership and asset management. Current trends show NFTs revolutionizing industries like gaming, music, and more.
Understanding NFTs and Digital Ownership
NFTs, or Non-Fungible Tokens, are transforming the way we perceive digital ownership. NFTs are unique, unlike other digital assets. They can’t be exchanged one-for-one like cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin. This section explains how NFTs change digital ownership. It also shows how blockchain makes this possible.
What Makes NFTs Unique?
NFTs have three standout qualities that make them different from cryptocurrencies. First, they are indivisible. Unlike a cryptocurrency, an NFT cannot be divided. A cryptocurrency, like Bitcoin, can be split into smaller units, called satoshis. An NFT remains whole and unique. Second, they are not interchangeable. Their non-fungibility gives them a unique blockchain ID. It lets anyone verify their ownership and authenticity. Third, NFTs provide a digital way to own art, music, virtual real estate, and other assets. This uniqueness offers opportunities for artists and collectors alike by ensuring scarcity and exclusivity in the digital world.
Blockchain and NFTs
Blockchain is the underlying technology that makes NFTs possible. It serves as a decentralized ledger that records all transactions related to an NFT, providing transparency and security. Each NFT is associated with a specific blockchain address and cannot be altered without consensus from the network. This ensures that ownership, provenance, and any subsequent sales of the NFT are fully traceable and immutable. Smart contracts on blockchains like Ethereum enable automatic royalty payments. They also enforce ownership terms. This makes NFTs a reliable way to manage digital assets.
Types of NFTs
NFTs can represent many types of digital assets. Digital art NFTs, like those from popular collections such as CryptoPunks or Bored Ape Yacht Club, are a prominent example. In the gaming world, NFTs allow players to own in-game assets such as characters, items, and even virtual real estate in games like Decentraland. The versatility of NFTs means they can be applied across multiple industries, from music to fashion, enabling new forms of digital engagement.
| Type of NFT | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Art NFTs | Represent unique digital artwork. | CryptoPunks, Bored Ape Yacht Club |
| In-Game Assets | Allow players to own assets within games, such as characters, items, or virtual real estate. | Decentraland |
| Music and Fashion | Enable artists and brands to create digital collectibles and new ways to engage with audiences. | Kings of Leon’s album NFT, Gucci’s digital sneakers |
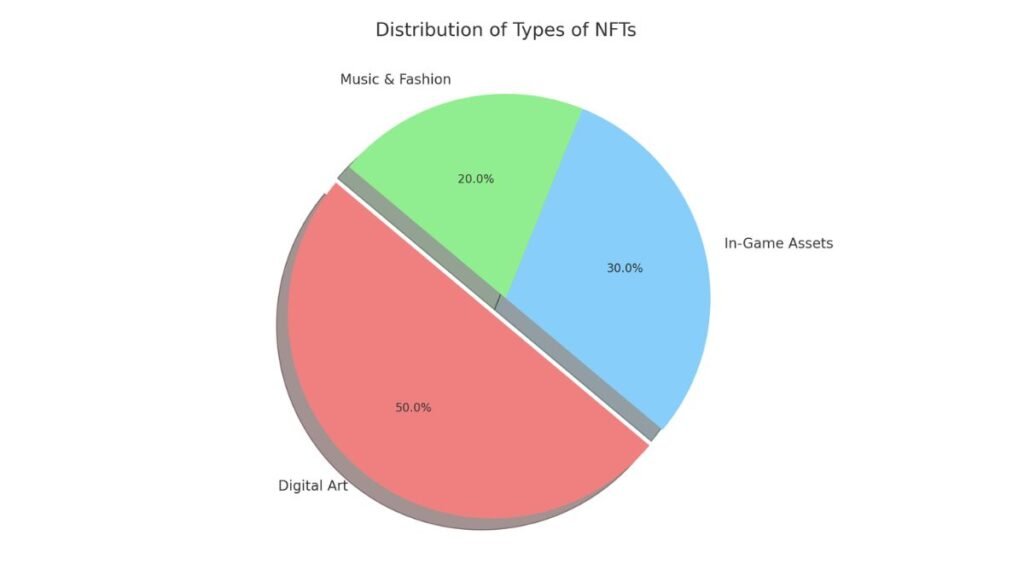
Here is a pie chart representing the different types of NFTs: Digital Art, In-Game Assets, and Music & Fashion. The chart shows the proportional distribution of these categories, highlighting Digital Art as the largest segment.
How NFTs Work and How to Get Started
For beginners, understanding the process of creating, buying, and storing NFTs is essential for managing these unique digital assets. NFTs are not just about ownership but also provide a new way for creators and collectors to engage in the digital economy. In this section, we’ll walk through the practical steps needed to get started with NFTs, from exploring NFT marketplaces to creating your own digital token.
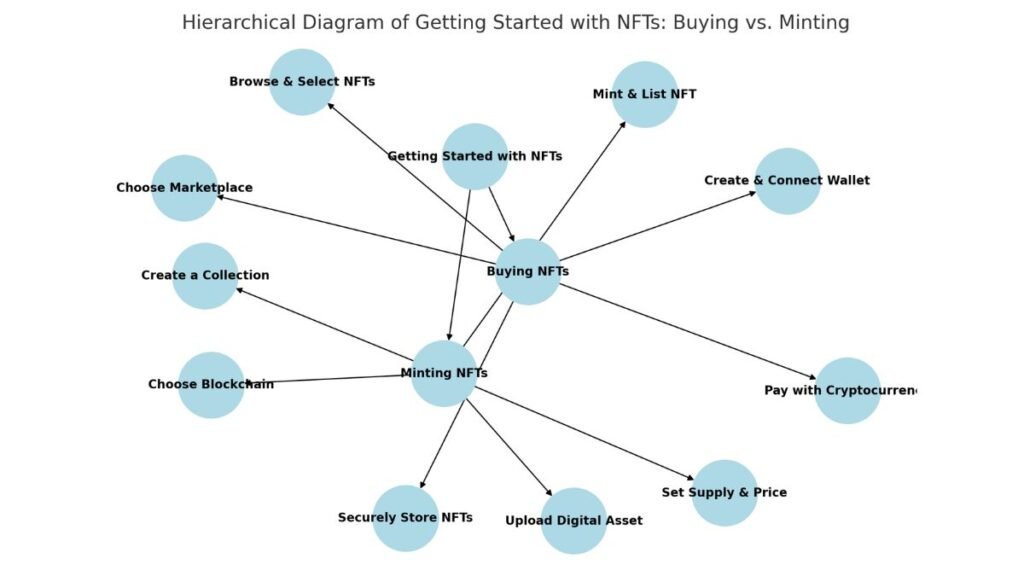
Here is a hierarchical diagram that represents the process of getting started with NFTs. It branches into two main paths: “Buying NFTs” and “Minting NFTs.” Each path contains the steps involved in the respective processes, providing a clear distinction between buying and creating NFTs.
NFT Marketplaces and How to Use Them
To get started with NFTs, the first step is to choose a marketplace. Popular NFT marketplaces like OpenSea and Rarible provide platforms for users to buy, sell, and trade NFTs. OpenSea, for instance, is the most beginner-friendly, supporting multiple blockchains like Ethereum and Polygon, and allowing payments via cryptocurrency or credit cards through third-party providers.
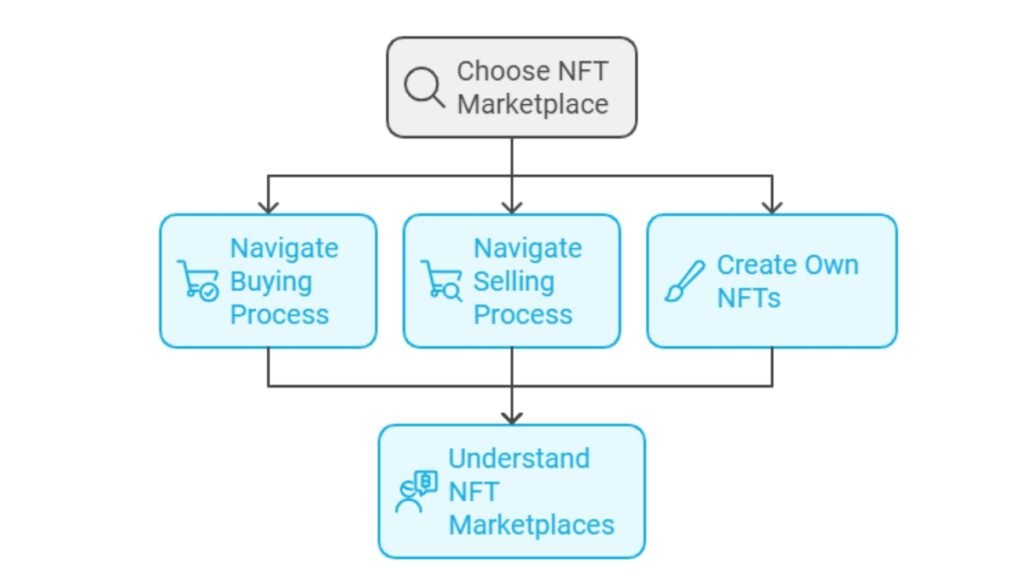
Step-by-Step Guide to Using NFT Marketplaces:
- Choose a Marketplace: Decide on an NFT marketplace like OpenSea or Rarible based on your needs and the type of NFTs you are interested in (e.g., digital art, gaming assets).
- Create and Connect a Wallet: You’ll need a cryptocurrency wallet (like MetaMask) that supports the blockchain the marketplace uses. Connect the wallet to the platform.
- Browse and Select NFTs: Use the marketplace’s search or explore tools to find NFTs. Look at their price, rarity, and creator details to ensure authenticity.
- Pay with Cryptocurrency: Most NFTs are purchased using cryptocurrency (like Ethereum), though some marketplaces allow credit card payments via services like MoonPay.
- Securely Store NFTs: Once purchased, the NFT will be stored in your wallet. Make sure to secure it with strong passwords and consider using a hardware wallet for added protection.
Creating and Minting NFTs
Minting an NFT refers to the process of creating a new digital asset on the blockchain. Platforms like OpenSea make it easy to mint your first NFT by guiding you through the steps of uploading your digital file and setting details like price and royalties.
How to Mint an NFT:
- Create a Collection: Start by creating a new collection on a marketplace like OpenSea. This allows you to organize your NFTs.
- Upload Your Digital Asset: Upload the media you want to tokenize (e.g., artwork, music, or video). Fill in details like the name, description, and any unlockable content.
- Set Supply and Price: Define how many NFTs you want to mint and set the price. You can choose a fixed price or set up an auction.
- Choose the Blockchain: Most NFTs are minted on Ethereum. Some platforms offer options like Polygon to cut gas fees.
- Mint and List: Once all the details are filled out, mint your NFT and list it on the marketplace for sale.
NFT Use Cases Across Industries
NFTs have moved beyond digital art. They now span gaming, music, and real estate. NFTs are reshaping industries and sparking new innovations. They do this by proving ownership, ensuring authenticity, and enabling direct creator-to-buyer connections.
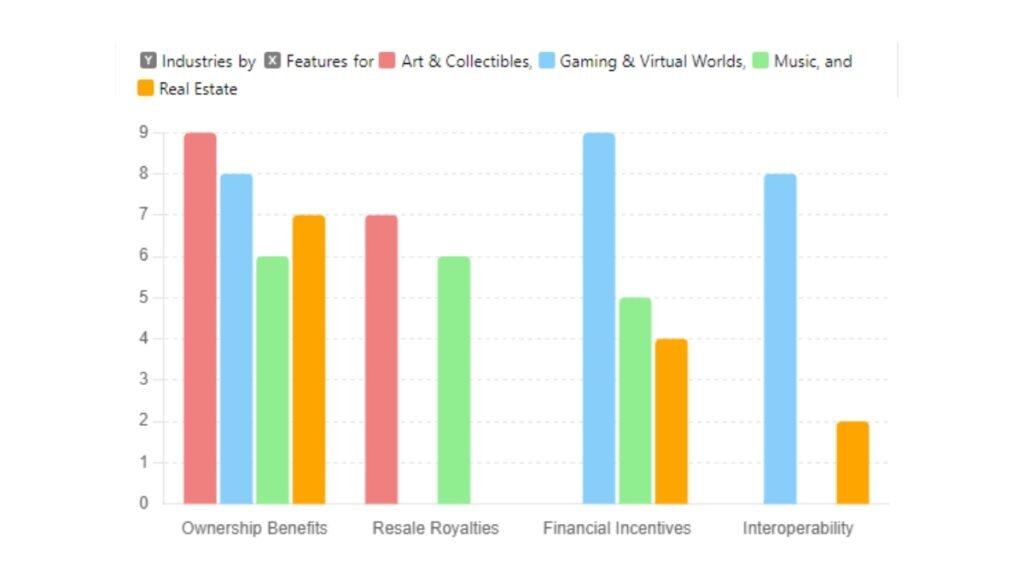
bar chart representing the use cases of NFTs across different industries. Each cluster of bars shows how features apply to these industries: Art & Collectibles, Gaming & Virtual Worlds, Music, and Real Estate. The features are ownership benefits, royalties, financial incentives, and interoperability.
NFTs in Art and Collectibles
NFTs have changed the art world. They let digital artists sell their work directly to consumers, without galleries or auction houses. Artists can retain control over resale royalties, ensuring continuous earnings as their works appreciate in value. High-profile NFT art sales, such as Beeple’s $69 million sale, have shown that NFTs can revolutionize art ownership and the global art market. This technology has democratized art. It lets more people buy, trade, and own unique digital assets.
NFTs in Gaming and Virtual Worlds
The gaming industry has quickly embraced NFTs. They give players ownership of in-game assets, like characters, skins, and virtual land. NFTs offer true ownership, meaning these assets can be traded or sold in and out of the game environment, providing players with financial incentives through the growing popularity of play-to-earn models. Also, cross-game interoperability lets gamers use their assets on multiple platforms. This expands the scope of virtual ownership.
NFTs in Music and Entertainment
NFTs are reshaping the music industry. They let artists tokenize their work. Now, they can sell albums, concert tickets, and exclusive experiences as NFTs. Musicians like Kings of Leon and 3LAU have successfully leveraged NFTs to monetize their content directly, creating new revenue streams while offering fans ownership of unique digital content. This shift lets fans engage more deeply with their favorite artists. It also lets artists control royalties and ticket sales.
Securing and Storing NFTs
Owning NFTs comes with the responsibility of protecting them from theft or loss. Proper storage and security measures are essential to ensure your valuable digital assets are safe. This section will explain different storage options and provide tips on how to secure your NFTs.
Choosing the Right Wallet
When it comes to storing NFTs, the two main wallet options are software wallets (hot wallets) and hardware wallets (cold wallets). Each has its advantages and disadvantages.
- Software wallets, such as MetaMask, are more convenient for users who frequently buy, sell, or trade NFTs. These wallets are connected to the internet, which makes them more vulnerable to hacking but easy to access from anywhere. They are ideal for active NFT market users. But, they only have basic security. They use encryption and a 12-24 word recovery phrase.
- Hardware wallets, like Ledger or Trezor, are the safest option. They store private keys offline, making them less vulnerable to hackers. Hardware wallets have features like biometric authentication, airgap technology, and PIN codes. Airgap tech keeps the device disconnected from external networks. They are ideal for long-term storage of valuable NFTs but are less convenient for regular trading due to the extra steps required for access.
Recommendation
For greatest security, use a hardware wallet. It’s best for holding NFTs long-term and for high-value digital assets.
Protecting Your NFTs from Scams
The NFT space, like the broader cryptocurrency world, is a target for various scams. To protect your NFTs, follow these guidelines:
- Verify Creator Legitimacy: Always research the creator of an NFT before making a purchase. Look for verified profiles and check previous sales to ensure the authenticity of the NFT.
- Check Previous Sales History: A blockchain explorer can confirm if the NFT has been traded before and its provenance.
- Use Trusted Marketplaces: Always buy NFTs from trusted platforms like OpenSea, Rarible, or Foundation. This reduces the risk of buying fake or plagiarized NFTs.
- Keep Wallet Private Keys Secure: Never share your wallet’s recovery phrase or private keys with anyone. It is recommended to store them offline, in a physical location like a safe, and avoid saving them digitally on your devices.
Additional Tips to Avoid NFT Scams:
- Be cautious of phishing links in emails, social media messages, and even Discord groups. Always double-check URLs to ensure you’re on legitimate websites.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) where possible to add an extra layer of security to your wallet.
Further Reading:
- NFT Marketplaces for Beginners – Learning Hub
- How to Mint NFTs on Ethereum – Learning Hub
- Top NFT Projects in 2024 – News
- NFT Security Best Practices – Tools
- Digital Art NFTs and Royalties Explained – Learning Hub
The Future of NFTs
NFTs are evolving rapidly, and 2024 is expected to bring several new trends that will shape their use and value. As the market matures, NFTs are moving beyond collectibles. They are now useful in the real world and are expanding into various industries. This section explores the future of NFTs and highlights key trends to watch.
Emerging Trends in NFTs
Several trends are expected to redefine the NFT landscape in 2024. Fractional ownership is gaining traction. It lets users buy shares in high-value NFTs, like digital real estate or rare artworks. It democratizes access to costly digital assets. It boosts NFT market liquidity. Investors can now own fractions of valuable NFTs without buying the whole asset.
Cross-chain compatibility is another important development. Transferring NFTs between blockchains, like from Ethereum to Solana, is boosting market access and liquidity. This tech is creating a more connected NFT ecosystem. It’s now easier to trade NFTs across platforms.
Addressing environmental concerns is also a priority. Eco-friendly blockchain networks, such as Algorand and Solana, are developing sustainable alternatives to energy-intensive systems. These green solutions will likely attract eco-friendly users. They will also reduce the carbon footprint of NFT transactions.
NFTs and Digital Identity
In 2024, NFTs are poised to play a growing role in digital identity, especially within the metaverse. NFTs can prove ownership of unique digital assets, like PFPs and virtual items. They verify a person’s digital presence and identity. Projects like CryptoPunks show that NFTs can be identity symbols in digital spaces. They grant users access to exclusive communities and experiences.
The integration of NFTs in the metaverse is also on the rise, with users able to own virtual land, fashion, and even digital avatars. NFTs provide verifiable proof of ownership in these virtual worlds, blending the digital and physical realms. As metaverse platforms continue to grow, NFTs will become a key tool for managing digital identities and assets.
NFTs have rapidly evolved, expanding beyond digital art into gaming, music, and virtual real estate. As the tech matures, trends are shaping the future. They are fractional ownership, cross-chain compatibility, and eco-friendly solutions. As NFTs become linked to digital identity in the metaverse, they offer new ways to own and express oneself in virtual spaces. As the market continues to innovate, NFTs will play an even more significant role in the digital economy.



















